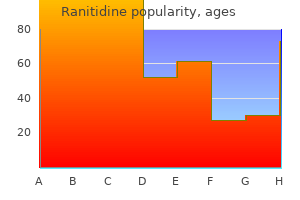
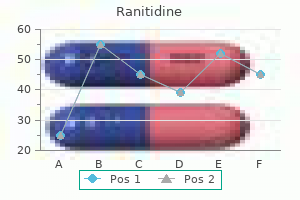
Ranitidine dosages: 300 mg, 150 mg
Ranitidine packs: 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
Order ranitidine 150 mg online
Unilateral choanal atresia may be manifested by a purulent nasal discharge on the affected aspect. Diagnosis: Both choanae in newborns should be routinely catheterized in the instant postnatal interval. Dysraphic anomalies of the anterior cranium base are caused by publicity to teratogenic agents during the second or third week of embryonic growth, when the neural tube is forming from the neural plate, or in the course of the fourth week, when the cerebral ventricles and central canal are forming and the central nervous system is separating from the epidermis and migrating to a deeper degree. Nasal dermoids, like dorsal nasal fistulas, are lined by keratinized squamous epithelium. Sites of predilection are the dorsal nasal midline and nasal flank, where the lesions current as cystic protrusions. Diagnostic catheterization or distinction injection is contraindicated as a outcome of the chance of intracranial complications. Treatment: Treatment consists of complete removing of the fistulous tract, which may embody excising the dural defect and repairing it by duraplasty. The fistula might terminate blindly and even prolong into the cranial cavity, creating an open communication with the subarachnoid house. Symptoms: Fistulas that terminate blindly are often manifested clinically at an older age due to inflammation across the fistulous opening. If the fistula communicates with the subarachnoid area, it might possibly lead to extreme problems corresponding to cerebrospinal fluid leakage, meningitis, or mind abscess. They closely resemble intranasal polyps and must be thought-about in the differential prognosis of kids with suspected nasal polyps, which are rare in this age group. Treatment: Treatment is always surgical and consists of eradicating the cephalocele and repairing the dural defect. Any associated anomalies of the orbit and facial skeleton must also be corrected. Cephaloceles are herniations of intracranial contents via a bony defect within the cranium. Several varieties are distinguished based on the structures concerned: meningocele (congenital protrusion of the leptomeninx), meningoencephalocele (leptomeninx and mind tissue), and meningoencephalocystocele (meningocele plus portions of the ventricular system). Classification: Cephaloceles of the anterior skull base are classified into two teams. Sincipital cephaloceles are situated close to the glabella, brow or orbit, while basal cephaloceles are discovered primarily within the nasal cavity or nasopharynx. The sincipital types seem as a pulsating mass close to the glabella, often related to a broad nasal dorsum and hypertelorism. For studying functions, nonetheless, septal deviation is classified as an intranasal deformity and is described separately from the various external deformities. A basic distinction is drawn between deformities of the external nose and intranasal deformities. They are incessantly mixed, however, as deformities of the external nose are usually related to a variable diploma of nasal septal curvature and should even be attributable to them. Symptoms: Almost everyone has some extent of bowing, spurring, or ridging of the cartilaginous or bony nasal septum. More pronounced degrees of septal curvature can impede nasal breathing and may trigger olfactory impairment due to inadequate air flow of the olfactory groove. Deficient nasal airflow can also lead to paranasal sinus sequelae similar to complications and recurrent sinusitis. A large septal spur that comes into contact with the nasal turbinates can cause epistaxis. Diagnosis: Septal subluxation is a particular kind in which the anterior septal margin is displaced from the median aircraft. The degree of nasal obstruction can be objectively evaluated by rhinomanometry (see p. For medicolegal reasons, olfactory testing should all the time be carried out previous to surgical remedy (see p. Treatment: the therapy of selection is surgical straightening of the deviated septum (septoplasty).
Ranitidine 150 mg order with visa
Subthalamic nucleus stimulation is favoured by most teams as a end result of, in distinction to pallidal stimulation, it permits patients to scale back their anti-Parkinsonian medication. Clinically, Parkinsonian sufferers can develop painful dystonic posturing of their limbs, which responds dramatically to bilateral pallidal stimulation. This has led to preliminary research of bilateral pallidal stimulation for dystonia, with promising outcomes. It started three years in the past and is growing in severity; whereas it affected her once a week initially, it now impacts her nightly. The resulting daytime sleepiness, anergy and fatigue have begun to interfere along with her daytime functioning, together with decreased reminiscence for current occasions, wordfinding difficulties, avoidance of social contact, low temper and decreased job performance. She obtains momentary reduction by stretching her extremities vigorously, rubbing them, using heat soaks or getting out of bed and walking round the home; nonetheless, the symptoms return shortly thereafter and awaken her repeatedly after sleep onset. Polysomnography reveals excessive proportions of stage 1 sleep, diminished proportions of slow-wave sleep, a number of awakenings and arousals and repetitive bursts of electromyographic exercise on lower limb leads, every lasting approximately 0. Core symptoms embody an irresistible urge to move the legs, arms or different physique components, with or with out uncomfortable or disagreeable sensations within the legs, starting or worsening in periods of relaxation or inactivity (lying, sitting). The symptoms are partially or totally relieved by motion (walking, stretching) and are worse within the evening or at evening. Associated findings include a constructive household history (prevalence in firstdegree relatives is three to 5 times higher than in those without restless legs syndrome), frequent response to dopaminergic therapy, periodic limb actions during sleep or wakefuless, a variable clinical course with frequent exacerbations and remissions, sleep disturbance and a traditional neurological examination. Recent mind imaging studies have revealed a significant lower in iron concentrations in iron-rich areas of the brain such as the substantia nigra and, considerably less significantly, the putamen. The connection between iron and dopamine is an elegantly easy one, as iron is a cofactor for the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase, which is concerned within the synthetic pathway of dopamine from tyrosine. Treatment with iron dietary supplements, though not indicated for restless legs syndrome, could be efficient. Two medicines used for therapy of this dysfunction are ropinirole and pramipexole. Sleep hygiene measures, including the avoidance of stimulants such as caffeine close to bedtime, also needs to be considered. Landmark publication setting out a conceptual framework for the way the basal ganglia and cerebral cortex process various sorts of information via largely distinct parallel circuits primarily based on identified anatomical connectivity. Subthalamic nucleus and its connections: anatomic substrate for the network effects of deep brain stimulation. The cerebral hemispheres develop from the sides of the telencephalon, every containing a lateral ventricle. The websites of evagination turn into the interventricular foramina, by way of which the two lateral ventricles and midline third ventricle communicate. The diencephalon corresponds largely to the constructions that develop lateral to the third ventricle. The lateral walls of the diencephalon type the epithalamus most superiorly, the thalamus centrally and the subthalamus and hypothalamus most inferiorly. The epithalamus in the mature mind incorporates the anterior and posterior paraventricular nuclei, the medial and lateral habenular nuclei, the stria medullaris thalami and the pineal gland. The thalamus undergoes proliferation to form quite a few nuclear lots that have in depth reciprocal connections with the cerebral cortex. The subthalamic region consists of the subthalamic nucleus, zona incerta and fields of Forel. The subthalamic nucleus is intently related to the basal ganglia and is considered with them in Chapter 14. The hypothalamic rudiment provides rise to a lot of the subdivisions of the grownup hypothalamus. The slim anterior pole lies near the midline and types the posterior boundary of the interventricular foramen. Posteriorly, an expansion, the pulvinar, extends past the third ventricle to overhang the superior colliculus. The brachium of the superior colliculus (superior quadrigeminal brachium) separates the pulvinar above from the medial geniculate physique under. A small oval elevation, the lateral geniculate body, lies lateral to the medial geniculate. It extends laterally from the line of reflection of the ependyma (taenia thalami) and types the roof of the third ventricle. This curved surface is separated from the overlying physique of the fornix by the choroid fissure, with the tela choroidea inside it.
Order ranitidine discount
The affected person was taken to surgical procedure where a perforated colon was found, most likely secondary to pseudomembranous colitis. The affected person was clinically doing nicely, and this was thought to represent benign pneumatosis. The highest density blood merchandise should be found adjacent to the positioning of bleeding. Note that the perihepatic hematoma is subtly denser than the perisplenic hematoma, suitable with the sentinel clot sign. Note the presence of a hematocrit stage inside the hemorrhage, a standard function with coagulopathic bleeds. This was found to be a large hepatic adenoma in a younger female affected person utilizing oral contraceptives. Adenoma and hepatocellular carcinoma are the most typical liver tumors to current with bleeding. Note that the tumor has bled into the perihepatic space with hematoma surrounding the proper liver lobe. Note the delicate gentle infiltration of the mesenteric fat throughout the abdomen, a standard characteristic of portal hypertension. Multiple mildly enlarged mesenteric nodes are present with a delicate surrounding "halo" of spared fat. Note the presence of stranding and infiltration extending medially into the sigmoid mesocolon. Note the presence of stranding and infiltration in the ileocolic mesentery near the terminal ileum. There is gentle infiltration of the adjoining proper decrease quadrant mesentery with fats stranding and irritation. Notice the profound infiltration and fats stranding throughout the left higher quadrant mesentery. The small bowel proximal to the mass is dilated, thickened, and hypoenhancing, appropriate with ischemia. There is intensive surrounding infiltration of the mesentery, in addition to bowel wall thickening. Notice the presence of ascites fluid adjacent to the omental tumor, in addition to insinuation amongst pelvic small bowel loops. Both findings are frequent and nonspecific in recipients of small bowel transplants and doubtless indicate some degree of rejection &/or lymphedema. The superior mesenteric vein (& portal vein) is thrombosed, and mesenteric edema is current. The highest density blood products are found adjacent to the liver damage (sentinel clot sign). Surrounding hemoperitoneum is also famous with a sentinel clot around the ruptured cyst. Hematocrit ranges are particularly frequent in the setting of coagulopathic bleeding. The mass has ruptured through the liver capsule with hemorrhage monitoring down the right paracolic gutter. These findings have been found to be secondary to hepatocellular carcinoma with rupture and hemorrhage. Incidentally, the liver is diffusely low density because of alcohol-related steatosis. Intraperitoneal bladder rupture, imaged after intravesical administration of distinction medium (cystography). Desmoid tumors can show variable enhancement, and in some circumstances, can be fairly avidly enhancing. Incidentally, a deep left gluteal lipoma has sign traits similar to regular subcutaneous fats. Abdominal wall endometriosis: clinical presentation and imaging options with emphasis on sonography. Although the hematoma is partly isodense to the muscle, the presence of a hematocrit stage makes the bleed more apparent. In this case, the left psoas muscle is atrophic due to a prior left leg amputation. The presence of psoas infection should all the time immediate cautious appraisal of the backbone.
300 mg ranitidine order mastercard
The extra-articular manifestations include: � uveitis (40%) � aortic regurgitation � symptoms of cauda equina syndrome (late) � higher lobe interstitial lung illness (late). Systemic lupus erythematosus this multisystem disorder occurs often in sufferers between 20 and forty years of age. The analysis requires no less than four of the 11 revealed standards either currently or in the past (Table 9. Drug-induced lupus is extra widespread within the elderly because of the extra frequent use of drugs in this group. Remember, newer antiarrhythmic and antihypertensive medicine have made classical drug-induced lupus less common and usually the signs resolve quickly with cessation of the drug; autoantibody levels (anti-histone) diminish slowly. Remember, though, that present remedy permits a 90% 10-year survival price compared with 50% 30 years in the past. This disfiguring skin illness leads to permanent hair loss with telangiectasia, scaling, circular erythematous lesions and follicular plugging. Look by the hands for vasculitis, which might produce nail-fold infarcts and ischaemia or gangrene, and rash. Look on the forearms for livedo reticularis and purpura on account of vasculitis or thrombocytopenia. Test for proximal myopathy brought on by precise disease or secondary to steroid remedy. Note any facial rash (butterfly photosensitivity rash (30%), discoid lupus or diffuse maculopapular rashes). In the cardiovascular system, observe signs of pericarditis or murmurs (Libman�Sacks endocarditis is a very unusual explanation for scientific signs). Note sparing of the proximal interphalangeal joints, tp:// eb oo ks m ed ebooksmedicine. Diagnosis is determined by a mixture of the symptoms, signs and laboratory take a look at outcomes (see Tables 9. In the respiratory system, notice signs of pleural effusion, pleuritis, interstitial lung illness or atelectasis. Examine for proximal weak spot in the legs, cerebellar ataxia, hemiplegia and transverse myelitis. Also study for neuropathy (mainly sensory) and mononeuritis multiplex, as well as thrombophlebitis and leg ulceration. Look on the urine analysis for proof of renal illness (haematuria and proteinuria). Also take a glance at the temperature chart for fever, indicating lively illness or secondary an infection. This affected person also has a haemorrhagic fundus er na l-m ed ic in e- vi de os 9 � the rheumatological long case 245 Table 9. Central nervous system symptoms typically correlate poorly with serological measures of the activity of the disease. Anaemia � normochromic, normocytic and associated to the chronic inflammatory processes � is fairly common. Leukopenia (especially lymphopenia) occurs in over half the patients and could also be caused by antibody directed against leukocytes. The lupus anticoagulant and anticardiolipin antibodies, or both, are present in about 10% of circumstances. Thrombocytopenia happens in 15% of cases and is associated with anti-platelet antibodies. There is a 90% 10-year survival fee; the main causes of demise are infections, renal failure, lymphoma and myocardial infarction. Hydroxychloroquine is very effective for skin and joint manifestations, reduces the danger of renal involvement and improves survival. Annual retinal and visual area examinations have to be performed in sufferers on this drug due to the cumulative threat of retinal toxicity. Steroids are indicated for central nervous system involvement, pericarditis, myocarditis, pleurisy, severe haemolytic anaemia and thrombocytopenia. Use of high preliminary doses with gradual discount as quickly as improvement happens is the proper technique of treatment.
Order genuine ranitidine
A 13-g coaxial needle has been advanced to the midline of the vertebral body (as decided by the location of the spinous process) via proper transpedicular method. This allows cement to fill bilateral features of the vertebral body, with out necessitating bilateral needle access. A hemostat marks the pores and skin access site, barely superior and lateral of the pedicle. Vertebroplasty, Transpedicular Approach (Fluoroscopic Alignment) Vertebroplasty, Transpedicular Approach (Advance Needle to Periosteum) (Left) An entry needle is advanced by way of the gentle tissues until bone is contacted. The needle tip must be positioned at the lateral edge of the pedicle at this point. The needle trajectory is in line to cross through the pedicle and avoid the intervertebral foramen. Vertebroplasty, Transpedicular Approach (Advance Needle to Periosteum) Vertebroplasty, Transpedicular Approach (Advance Needle to Vertebral Body) (Left) As the needle is superior through the pedicle, it should not cross the medial or inferior facet of the pedicle. To do so would danger harm to spinal nerves, or to the spinal twine itself depending on the vertebral degree accessed. Vertebroplasty, Transpedicular Approach (Advance Needle to Vertebral Body) 664 Vertebral Augmentation and Sacroplasty Neuroradiology Procedures Vertebroplasty, Transpedicular Approach (Midline Needle Tip Position) Vertebroplasty, Transpedicular Approach (Midline Needle Tip Position) (Left) In a unique patient at thoracic level, the needle is advanced to midline of vertebral body if attainable. Alternate Bipedicular Approach (Proper Needle Position) Alternate Bipedicular Approach (Proper Needle Position) (Left) Bipedicular needle entry is often fascinating when treating lumbar vertebra. Alternate Curved Curette (Cement Delivery) Alternate Curved Curette (Lateral Radiograph) (Left) Rather than positioning the needle at midline, which risks crossing medially of the pedicle throughout advancement, the entry needle could remain ipsilateral to access. The curette may be used to make a cavity, or cement could also be injected through the curette permitting more accurate cement deposition throughout vertebroplasty. Tracks for kyphoplasty balloon may be created by advancing needle tricks to the anterior 1/3 of the vertebral body and then withdrawing the outer cannulas, or by advancing metallic drills (included in kit) through the cannulas into the vertebral physique. Kyphoplasty (Balloon Insertion) Kyphoplasty (Balloon Inflation) (Left) the kyphoplasty balloon is slowly inflated with iodinated distinction materials using an inflator with a calibrated manometer. The balloon inflation creates a void within the cancellous bone prior to cement delivery and will end in some height restoration to the vertebra. Kyphoplasty (Balloon Inflation) Kyphoplasty (Bipedicular Balloon Inflations) (Left) Bilateral transpedicular kyphoplasty balloons have been inflated with iodinated distinction. Both unipedicular and bipedicular approaches could additionally be used for kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty. Beveled needle ideas can redirect needles at risk for traversing foraminal or sacral cortex. Final imaging shows cement properly distributed via the sacral ala without extension into sacral foramen or outdoors of sacral cortex. The entry needle is seen inside the sacrum following placement with longitudinal trajectory. Sacroplasty: Fluoroscopic-Guided Cement Injection (Sagittal) Kiva Vertebral Compression Fracture Treatment System (Implant Deployment) (Left) Kiva is an alternate vertebral augmentation system whereby a coil-shaped implant is delivered into the vertebral body over a guidewire (subsequently removed), which had been inserted through the transpedicular access needle. The implant is designed to limit cement extravasation outside of the vertebral body. Fluoroscopic imaging obtained at the time of the procedure reveals earlier remedy of T10 and L1, in addition to the brand new treatment of T12. Always contemplate the potential for new fracture in sufferers whose ache fails to improve or returns following remedy. Complication: Fracture Retropulsion Complication: Intrapulmonary Cement Embolization (Left) Retropulsion of a pathologic vertebral fracture occurred during kyphoplasty. Kyphoplasty can displace tumor into the spinal canal during balloon inflation, causing spinal twine damage. There is infectious phlegmon throughout the epidural area with a ventral epidural abscess. The renal artery and vein are anastomosed to the recipient exterior iliac vessels. Definitive imaging and potential remedy could additionally be indicated through endovascular means. Hydronephrosis usually outcomes from ureteral stricture associated to ischemia or ureteral compression from perigraft collections. Copelan A et al: Iatrogenic-related transplant injuries: the function of the interventional radiologist.
Mexican Chilies (Capsicum). Ranitidine.
- Nerve pain (neuropathy) in people with diabetes when applied to the skin.
- How does Capsicum work?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Back pain.
- Arthritis pain when applied to the skin.
- Colic, cramps, toothache, blood clots, fever, nausea, high cholesterol, heart disease, stomach ulcers, heartburn, irritable bowel syndrome, migraine headache, allergic rhinitis, perennial rhinitis, nasal polyps, muscle spasms, laryngitis, swallowing dysfunction, and other conditions.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96908
Ranitidine 300 mg without a prescription
Mossy fibres take their origin from the spinal wire, trigeminal, dorsal column and reticular nuclei of the medulla and from the pontine tegmentum and basal pons. As each mossy fibre traverses the white matter, its branches diverge to enter a quantity of adjoining folia. Within each folium, these branches expand into grape-like synaptic terminals (mossy fibre rosettes) that occupy the centre of cerebellar glomeruli. Noradrenergic and serotoninergic fibres type a rich plexus in all layers of the cerebellar cortex. The aminergic fibres are fantastic and varicose and type intensive cortical plexuses; their release of noradrenaline (norepinephrine) and serotonin is assumed to be non-synaptic, and their effects are paracrine, involving volumes of tissue. The serotoninergic afferents of the cerebellum take their origin from neurones within the medullary reticular formation, aside from the raphe nuclei. The noradrenergic, coeruleocerebellar projection, when energetic, inhibits Purkinje cell firing not by direct action but by -adrenergic receptor�mediated inhibition of adenylate cyclase within the Purkinje cells. Cerebellar afferents have been traced from dopaminergic cells in the ventral tegmental area, and dopamine D2 and D3 receptors are present in the molecular layer. A comparable plexus of thin, choline acetyltransferase�containing fibres is centred on the Purkinje cell layer. The connections of the cerebellum are organized in two perpendicular planes, corresponding to the planar group of the cerebellar cortex. Efferent connections of the cortex are disposed in parasagittal sheets or bundles that connect longitudinal strips of Purkinje cells with particular cerebellar or vestibular nuclei. The climbing fibre afferents to a Purkinje cell zone from the inferior olive display an analogous zonal disposition. Cerebellar output is organized in modules, with a module consisting of a number of Purkinje cell zones, their cerebellar or vestibular target nucleus and their olivocerebellar climbing fibre input. Modular perform is determined by the brain stem projections of the cerebellar or vestibular target nucleus. Mossy fibre afferent techniques from precerebellar nuclei within the spinal cord and the mind stem terminate in the granular layer of certain lobules in transversely oriented terminal fields. The transverse lobular arrangement of the mossy fibre afferents is enforced by the transverse orientation of the parallel fibres, which are axons of the granule cells and constitute the second hyperlink within the mossy fibre�parallel fibre enter of the Purkinje cells. Parallel fibres cross and terminate on Purkinje cells belonging to a quantity of successive modules as they course via the molecular layer. Granule cell activity generates easy spikes, which resemble the response of different neurones within the mind, whereas activation by a climbing fibre produces a prolonged depolarization on which several spike-like waves are superimposed. Whereas the Purkinje cell could fire simple spikes at a price of hundreds per second, complicated spikes happen at very low frequencies, seldom more than three or 4 per second. Like Purkinje cells, Golgi cells have a wealthy dendritic tree that extends via the molecular layer. Golgi cells regulate firing by presynaptic inhibition of the mossy fibre afferents, so that they act as a governor, or price limiter, of Purkinje cell exercise. Stellate and basket cells synapse instantly on Purkinje cells and are highly effective inhibitors of their activity. The efferent pathways of these areas monitor the activity in the corticospinal tract and within the subcortical motor methods descending from the vestibular nuclei and reticular formation. The inputs to the cerebellum and the outputs from it are organized in accordance with the identical somatotopic patterns, however the orientation of these patterns is reversed. The illustration of the pinnacle is found principally in the easy lobule and caudally in a corresponding region of the posterior lobe. Vestibular connections of the cerebellum show a similar double illustration in the most rostral lobules of the anterior lobe and far caudally in the vestibulocerebellum. The folium, tuber, uvula, tonsil and posterior biventral lobule all obtain an nearly pure pontine mossy fibre input. Climbing fibres from the inferior olive and mossy fibres from the basilar and tegmental pontine nuclei relay visible and acoustic data from the respective cerebral association areas and midbrain tectum to the folium and tuber that are thought to symbolize a vermal visible and acoustic space. The efferent connections of this space travel by way of the fastigial nucleus to gaze centres in the pons and midbrain. Her gait is broad primarily based and unsteady, and she or he has impaired dexterity in the right hand, with nearly unintelligible handwriting and a prominent crescendo intention tremor on the best finger-to-nose check. Imaging demonstrates a large cystic lesion in the right cerebellar hemisphere, with compression of the fourth ventricle and secondary enlargement of the aqueduct and the lateral ventricles. At surgery, a well-defined mass is found at the margin of the cyst, a so-called mural nodule with the histological characteristic of a low-grade astrocytoma.
Purchase ranitidine master card
The arteries show a good fluorescence, however the veins appear striped, owing to laminar circulate. B, Angiogram of the left optic disc, showing the major arteries and veins and likewise their smaller branches. The topic is an elderly individual with considerable macular pigmentation, which masks fluorescence from the choroidal circulation. D, Angiogram of the macula of a younger subject (left eye) showing the macular capillaries intimately. Pigment cells lie behind the retina, and a quantity of other forms of retinal glial cell are distributed in distinctive areas amongst its different layers. Layer 2: Rod and Cone Cell Processes - this accommodates the photoreceptive outer segments and the outer elements of the internal segments of rod and cone cells. Layer three: External Limiting Membrane - this layer appears as a definite line by mild microscopy. It consists of a zone of intercellular junctions of the zonula adherens type between the processes of radial glial cells and photoreceptor processes. Layer four: Outer Nuclear Layer - this consists of several tiers of rod and cone cell bodies and their nuclei, the cone nuclei lying outermost. Mingled with these are the outer and inside fibres from the same cell our bodies, directed outward to the bases of inner segments and inward toward the outer plexiform layer. Layer 5: Outer Plexiform Layer - this may be a area of complex synaptic arrangements between the processes of cells whose cell bodies lie in the adjoining layers. The outer plexiform layer incorporates the synaptic processes of rod and cone cells, bipolar cells, horizontal cells and some interplexiform cells (which, in this account, are grouped with the amacrines). Horizontal cell nuclei form the outermost zone; then, in sequence inward, are the nuclei and cell our bodies of bipolar cells, radial glial cells and the outer set of amacrine cells, including the interplexiform cells whose dendrites cross this layer. Layer 7: Inner Plexiform Layer - that is divisible into three layers, depending on the forms of contact that happen. Its internal regions include the cell our bodies, nuclei and initial segments of retinal ganglion cells of varied courses. Layer 9: Nerve Fibre Layer - this incorporates the unmyelinated axons of retinal ganglion cells. It varieties a zone of variable thickness over the internal retinal surface and is the one part of the retina on the point where the fibres pass into the nerve at the optic disc. The inner side of this layer accommodates the nuclei and processes of astrocytes, which, along with radial glial cells, ensheathe the nerve fibres. Between the nerve fibre layer and the ganglion cells is another narrow innermost plexiform layer, the place neuronal processes make synaptic contact with axon hillocks and initial segments of ganglion cells. Layer 10: Internal Limiting Membrane - this is a glial boundary between the retina and the vitreous physique. It is shaped by the end-feet of radial glial cells and astrocytes and is separated from the vitreous body by a basal lamina. Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells - the retinal pigment epithelial cells are low cuboidal cells that type a single continuous layer, extending from the periphery of the optic disc to the ora serrata and proceed from there into the ciliary epithelium. Apically (toward the rods and cones), the cells bear long (5 to 7 mm) microvilli that contact or project between the outer ends of rod and cone processes. The tips of rod outer segments are deeply inserted into invaginations in the apical membrane. The attachments are unsupported by junctional complexes and are damaged within the scientific condition of retinal detachment arising from trauma or disease processes. Pigment epithelial cells play a major function within the turnover of rod and cone photoreceptive elements. Their cytoplasm incorporates the phagocytosed ends of rods and cones undergoing lysosomal destruction. The final products of this process are lipofuscin granules, which accumulate in these cells and add to their granular appearance.
Ranitidine 150 mg purchase on-line
Discussion: the mix of history, neurological examination and diagnostic check results factors strongly to a analysis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob illness, a human prion disease and one of many so-called transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. Anatomically, the disorder entails gray matter diffusely all through the neuraxis, with remarkable devastation. There is hanging loss of neurones within the cerebral cortex, with a brisk astrocytic response and microcavitation (spongiform encephalopathy). New perspectives in basal forebrain group of special relevance for neuropsychiatric disorders: the striatopallidal, amygdaloid and corticopetal components of the substantia innominata. Provides evidence that the region of the substantia innominata within the basal forebrain is composed of components of three forebrain constructions: the ventral striatopallidal system, the prolonged amygdala and the magnocellular corticopetal system. Pain processing during three levels of noxious stimulation produces differential patterns of central exercise. Classic description of the organization of sensory and motor homunculi within the human cerebral cortex. It is situated within the neck opposite a line drawn down the facet of the neck from the basis of the auricle to the extent of the higher border of the thyroid cartilage. It is deep to the internal jugular vein, the deep fascia and sternocleidomastoid, and anterior to scalenus medius and levator scapulae. Each ramus, besides the first, divides into ascending and descending parts that unite in communicating loops. From the primary loop (C2 and C3), superficial branches provide the pinnacle and neck; cutaneous nerves of the shoulder and chest come up from the second loop (C3 and C4). The superficial branches perforate the cervical fascia to supply the pores and skin, whereas the deep branches generally supply the muscles. The superficial branches both ascend (lesser occipital, great auricular and transverse cutaneous nerves) or descend (supraclavicular nerves). Descending under platysma and the deep cervical fascia, the trunk divides into medial, intermediate and lateral (posterior) branches, which diverge to pierce the deep fascia slightly above the clavicle. The medial supraclavicular nerves run inferomedially across the exterior jugular vein and the clavicular and sternal heads of the sternocleidomastoid to provide the skin so far as the midline and as low as the second rib. The intermediate supraclavicular nerves cross the clavicle to provide the skin over pectoralis major and deltoid down to the extent of the second rib, next to the realm of supply of the second thoracic nerve. The lateral supraclavicular nerves descend superficially throughout trapezius and the acromion, supplying the skin of the higher and posterior parts of the shoulder. It curves around the accent nerve and ascends along the posterior margin of the sternocleidomastoid. Near the skull it perforates the deep fascia and passes up onto the scalp behind the auricle. It provides the pores and skin and connects with the great auricular and higher occipital nerves and the auricular branch of the facial nerve. Its auricular branch provides the skin on the higher third of the medial side of the auricle and connects with the posterior department of the nice auricular nerve. It has been advised that compression or stretching of the lesser occipital nerve contributes to cervicogenic headache. It arises from the second and third cervical rami, encircles the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid, perforates the deep fascia and ascends on the muscle beneath platysma with the exterior jugular vein. The anterior branch is distributed to the facial pores and skin over the parotid gland, connecting in the gland with the facial nerve. The posterior department communicates with the lesser occipital nerve, the auricular branch of the vagus nerve and the posterior auricular branch of the facial nerve. Communicating branches move from the loop between the primary and second cervical rami to the vagus and hypoglossal nerves and to the sympathetic trunk. The hypoglossal department later leaves the hypoglossal nerve as a collection of branches-namely, the meningeal, superior root of ansa cervicalis and nerves to thyrohyoid and geniohyoid. It perforates the deep cervical fascia and divides beneath platysma into ascending and descending branches that are distributed to the anterolateral areas of the neck. The ascending branches ascend to the submandibular region, forming a plexus with the cervical branch of the facial nerve beneath platysma.
Real Experiences: Customer Reviews on Ranitidine
Mirzo, 60 years: The small bowel proximal to the mass is dilated, thickened, and hypoenhancing, compatible with ischemia. A tonotopic representation has not been described on this subdivision, and cells within the dorsal nucleus respond to a broad vary of frequencies.
Cobryn, 57 years: He remained basically asymptomatic, & the pneumatosis was attributed to his immunosuppressive medications. Involvement of the exterior nostril is called lupus pernio as a outcome of the characteristic skin modifications resemble chilblains (pernio).
Fraser, 55 years: Note the ancillary options of cirrhosis and portal hypertension, which probably predisposed the patient toward growing this aneurysm and thrombosis. At the site of compression, the frequent peroneal nerve could additionally be affected in its entirety, or the superficial or deep peroneal branches may be affected alone.
Thordir, 25 years: There is decreased sensation within the left medial higher arm, forearm and hand, involving particularly the fifth digit. The fasciculi may be conspicuous enough to give tendons a longitudinally striated appearance to the unaided eye.
Lars, 26 years: There is biliary ductal dilatation as a result of a standard duct stricture, through which the drain has been passed. Electroencephalogram reveals impartial bitemporal periodic lateralizing epileptiform discharges and mild generalized background slowing.
Rune, 62 years: The olfactory cortex has connections with the tertiary olfactory facilities (including the hippocampus, anterior insular region, and reticular formation), that are believed to have polysensory associative functions. The investigations the patient has undergone or could also be about to bear may help kind out the prognosis.
Umbrak, 63 years: The inferior olivary complicated and its climbing fibres may be activated by tactile, proprioceptive, visual and vestibular stimulation and from the sensory, motor and visual cortices and their brain stem relays. His postoperative course was sophisticated by a period of bowel obstruction and he required parenteral feeding for 10 days.
10 of 10 - Review by R. Trano
Votes: 119 votes
Total customer reviews: 119
References
- Tuman KJ, McCarthy RJ, Najafi H, et al: Differential effects of advanced age on neurologic and cardiac risks of coronary artery operations, J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 104:1510-1517, 1992.
- Hashitani H: Interaction between interstitial cells and smooth muscles in the lower urinary tract and penis, J Physiol 576(Pt 3):707n714, 2006.
- McCaughan BC, Martini N, Bains MS. Bronchial carcinoids. Review of 124 cases. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1985;89(1):8-17.
- Mercuri E, Brockington M, Straub V, et al. Phenotypic spectrum associated with mutations in the fukutin-related protein gene. Ann Neurol. 2003;53(4):537-542.
- Crucitti A, Feliciani C, Grossi U, et al. Paraneoplastic acrokeratosis (bazex syndrome) in lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 2009;27(36):e266-e268.
- Tsao MS, Schraufnagel D, Wang NS. Pulmonary metastasis of choriocarcinoma with a miliary roentgenographic pattern. Arch Pathol Lab Med 1981;105:557-8.