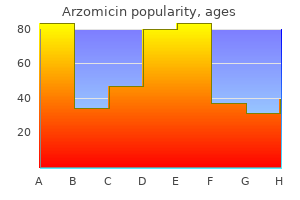
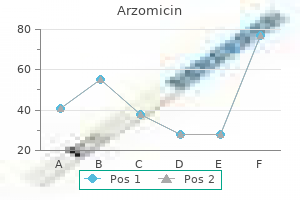
Arzomicin dosages: 500 mg, 250 mg, 100 mg
Arzomicin packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
Order arzomicin visa
Due to these reasons and to avoid harm to the phrenic nucleus, a surgical method on the T1 spinal section is more preferable. In this process, a needle is launched into the anterolateral quadrant of the spinal twine by way of the intervertebral area between the atlas and the axis. To stop any serious adverse effects, an electrode could also be passed via the needle. The path of the needle and the stimulating electrode are monitored through imaging methods. Any motor response from the ipsilateral upper or lower extremity should be considered a serious sign that the needle has entered the lateral corticospinal tract and that it have to be rerouted. Tingling sensations are normally felt because the needle enters the lateral spinothalamic tract, which is the site of cordotomy. Since fibers of the lateral spinothalamic tract ascend two to three segments within the dorsolateral tract of Lissauer earlier than coming into the dorsal gray column, the anesthesia induced by this process will begin 4 to eight segments below the extent of cordotomy, and due to this fact, the pain from the higher extremity may not be abolished fully. The first-order neurons for these pathways are situated in the sensory ganglia of the trigeminal, facial, glossopharyngeal, and vagus nerves. Depending upon the modality of sensation, the central processes of the ganglionic neurons enter the brainstem, establishing synapses with the sensory nuclei of the trigeminal nerve. Fibers conveying nociceptive, thermal and some tactile sensations type the spinal trigeminal tract and synapse in the spinal trigeminal nucleus. Pressure and tactile fibers terminate within the principal sensory nucleus, whereas proprioceptive fibers are transmitted to the mesencephalic nucleus. The axons of the neurons of the spinal trigeminal nucleus and the principal sensory nuclei type the dorsal and ventral trigeminal tracts. The ventral trigeminal lemniscus (tract) is a crossed tract, which originates from the spinal trigeminal nucleus and the ventral part of the principal sensory nucleus. These ascending thalamocortical fibers occupy the posterior limb of the internal capsule. Damage to the ventral trigeminal tract could happen in lesions of the pontine and midbrain tegmentum, resulting in contralateral lack of ache, thermal, and, to a point, tactile sensation from the facial region. Axons, which are derived from the dorsal part of the principal sensory nucleus, the place the mandibular nerve fibers terminate, form the ipsilateral dorsal trigeminal lemniscus (tract). Destruction of the dorsal trigeminal tract ends in ipsilateral lack of pressure and tactile sensation. The spinocerebellar tracts project to the spinocerebellum (anterior lobe of the cerebellum), carrying proprioceptive, stretch, and tactile sensations. They include the dorsal and ventral spinocerebellar, cuneocerebellar, and rostral spinocerebellar tracts. It is an ipsilateral tract that ascends near the surface of the dorsolateral funiculus and enters the spinocerebellum (anterior lobe of the cerebellum) via the inferior cerebellar peduncle. This tract carries proprioceptive, tactile, and strain impulses from particular person muscles and joints of the lower limb and lower half of the trunk. The higher limb equal of the dorsal spinocerebellar tract is the cuneocerebellar tract, which originates from the accent cuneate nucleus and terminates ipsilaterally within the spinocerebellum and pontocerebellum (anterior and posterior lobes of the cerebellum) via the inferior cerebellar peduncle. The ventral spinocerebellar tract is derived from the gray columns of the intermediate and the border cells of the ventral gray column in the thoracic, lumbar, and sacral segments. It is a crossed tract, conveying proprioceptive information from the whole lower extremity, significantly from the internuncial neurons that mediate flexor reflexes and provide input to the cerebellum. It also conveys info from the collateral of primary afferents emanating from the muscles and joints of the decrease extremity. This pathway reaches the contralateral anterior lobe of the cerebellum by way of the superior cerebellar peduncle. The higher limb equivalent of this tract is the ipsilateral rostral spinocerebellar tract, which arises from laminae Vll of the cervical enlargement and upper thoracic spinal segments. It enters the cerebellum by way of the inferior and superior cerebellar peduncles to be distributed to the anterior lobe of the cerebellum.
Best arzomicin 250mg
In the exudative sort, there shall be modifications within the visible hyperacuity (ability to determine misalignment of visible objects) before any modifications within the visible acuity, and this may be assessed by preferential hyperactivity perimetry. In the advanced stage of the disease, irreversible damage happens to the photoreceptors and leads, although rarely, to blindness. Dark or coloured spot within the heart of the visible field is referred to as central scotoma. The level of exit of axons of the optic nerve from the eyeball marks the optic disc of the retina, generally known as the blind spot. The focal blind spot attributed to the optic disc is termed physiological scotoma. Arcuate scotoma is a pathological focal visual deficit, which ends up from a lesion within the retina or optic nerve fibers. It occurs near the optic disc and arches superiorly or inferiorly toward the nasal field of the retina and in the path of the axons of the ganglionic multipolar neurons. Scintillating (flittering) scotoma (teichopsia) is characterized by floating of irregular and lucid spot, typically with a zigzag or wall-like outline, which may final for as a lot as 20 to 25 min. Patients could exhibit blindness to all colors (achromatopia) or to one (monochromatopia) or two colours (dichromatopia). The inherited variation in the amount of photopigments within the blue cones, green cones, and red cones may account for the sex-linked condition of shade blindness. This is due to the truth that pink and green genes exist as a recessive trait on the male X chromosome. One p.c of males lack the purple gene (protanopes-lack the long-wave mechanism), Visual System 327 and 2%�3% lack the green gene (deuteranopes-lack the medium-length mechanism). The pink gene could have given rise to the blue cone pigment, which, in flip, has given origin to the red and green cone pigments. Trichromats are individuals with normal three-color imaginative and prescient or with one normal shade vision and two feeble pink imaginative and prescient (protanomaly). Trichromats may also have three feeble green imaginative and prescient (deuteranomaly) or four weak blue imaginative and prescient (tritanomaly). These weaknesses are because of the reduction within the amount of cone pigment and are unrelated to neuronal circuitry associated with processing of the colour imaginative and prescient. Dichromats, people with two-color imaginative and prescient (color blind) and who lack one of the pigments, may not understand pink (protanopes) because of an absence of erythrolabe, green (deuteranopes) because of absence of chlorolabe, or blue (tritanopes-lack the short-wave size mechanism) as a result of the absence of cyanolabe. Gene loss or recombination between genes, which produces a hybrid gene on the X chromosome, could occur in people with red�green color blindness. Pathological circumstances that have an result on the outer layer of the retina may produce blindness to blue shade (tritanopia) on account of loss of the processing mechanism of short-wave length. In this fashion, pathological components that affect the optic nerve and the inner retinal layer might cause lack of red�green colour imaginative and prescient. Progressive nyctalopia (night blindness) and ring scotoma are circumstances in which the center and excessive peripheral a part of the retina are spared while the mid portion of the periphery is affected to a great extent. A small lesion or petechial hemorrhage within the retina close to the optic disc produces a focal blindness or scotoma by which central visual acuity is impaired. Darkness causes vitamin A to undergo reverse adjustments into retinin, which bonds with opsin to form rhodopsin. They stimulate the "on"-type ganglionic cells and are launched from inhibition by illumination. Hyperpolarizing (flat) neurons, which are inhibited by light, excite the "off"-type ganglionic neurons, maintaining totally different receptors. The nuclei of these neurons are positioned in the internal nuclear layer, whereas the axons are spread within the internal plexiform layer, establishing contacts with the dendrites of the ganglion cells. These cells contain completely different transmitters and, together with the ganglionic neurons, are the only excitable (produce action potentials) neurons of the retina. The horizontal cells set up inhibitory dendrodendritic synapses with the bipolar neurons, intensifying distinction by inactivating the bipolar and ganglionic neurons. They are either "on" sort or "off" kind, dependent upon their synaptic connections with the bipolar neurons.
Syndromes
- Certain types of vascular stents
- CSF examination for cell count, glucose, and protein
- Age over 40
- Stupor (a lack of alertness)
- Time it was swallowed
- Leakage of fluid from the new pancreas where it attaches to the intestine or bladder
Order generic arzomicin line
Dysfunction of the vestibular nerve produces ataxia, vertigo, and nystagmus, that are briefly defined beneath (see also the vestibular system, Chapter 15). A central infarct localized within the brainstem causes dysmetria, diplopia, dysarthria, dysphagia, and paresis or numbness across the mouth. Peripheral vestibular lesions are normally associated with a mild degree of disequilibrium. Ataxia (incoordination of motor activity) due to vestibular nerve dysfunction, is a severe and gravity dependent condition that often manifests as an intermittent incoordination of limb actions and turns into obvious throughout walking and standing. Vertigo is a extreme sense of rotation of the surroundings which is incessantly intermittent and could also be accompanied by oscillopsia (a back-and-forth movement of the visible objects with downbeat nystagmus), nausea, and vomiting. In peripheral vestibular dysfunction, vertigo is attributable to unilateral interruption of the tonic vestibular impulses. Head stability requires a discount within the firing fee from one horizontal duct coupled with increased firing price from the contralateral aspect. When this steadiness is disturbed with a peripheral vestibular lesion, the firing price on the affected aspect is lowered, which is interpreted as head turning. Nystagmus, an irregular rhythmic oscillation of the eyeball, is produced visually by watching stationary targets from a transferring automobile (optokinetic nystagmus) or by excessive gaze to one facet. It may also be produced iatrogenically by instilling cold or heat water into the ear (caloric test) or rotating in the Barany chair. Clinically, it may outcome from peripheral or central vestibular lesions (see also the vestibular system, Chapter 15). In a unilateral peripheral vestibular lesion, the firing rate of the horizontal semicircular canal is lowered, causing slow eye motion (slow section of nystagmus) toward the affected facet adopted by corrective fast eye movement (rapid phase of nystagmus) phase to the contralateral side. This nystagmus, which is gaze dependent, turns into more pronounced when the patient seems toward the affected aspect. The site of entry of the cochlear nerve into the pons and its course throughout the inner acoustic meatus are identical to that of the vestibular nerve. The dendrites of the bipolar neurons of the spiral ganglia obtain auditory impulses from the organ of Corti (site of auditory neuroepithelial cells) within the cochlea and convey these impulses to the dorsal and ventral cochlear nuclei within the caudolateral part of the pons. Postsynaptic fibers synapse in the ipsilateral and contralateral superior olivary nuclei, while others continue to the opposite side, ascending within the lateral lemniscus. Postsynaptic neurons of the superior olivary nuclei project throughout the ipsilateral lateral lemniscus to the inferior colliculus. Fibers from the inferior colliculus travel rostrally to the medial geniculate nucleus and then via the auditory radiation to the transverse gyri of Heschl. Damage to the cochlear nerve, on account of acoustic neuroma, or fracture involving the petrous temporal bone, produces sensorineuronal deafness on the facet of the lesion. This kind of deafness could additionally be accompanied by tinnitus and is distinguished from conduction deafness by Rinne and Weber tests (see the auditory system, Chapter 14). Tinnitus refers to a unilateral or bilateral situation that ranges from a delicate hissing sound or ringing noise to devastating loud fixed roaring. It could additionally be continuous or intermittent and is a crucial manifestation of harm to the cochlear nerve. Fractures of the posterior cranial fossa involving the interior acoustic meatus and tumors of the cerebellopontine angle (acoustic neuroma) might lead to mixed vestibular, cochlear, and facial nerve dysfunctions. This type of injury is characterised by deafness on the side of the lesion, vertigo (sense of rotation of the setting or self), nystagmus, ataxia, and signs of ipsilateral infranuclear facial palsy. It has two ganglia, a superior somatic sensory and an inferior visceral sensory ganglia. This nerve gives off tympanic, carotid sinus, lingual, pharyngeal, tonsillar, muscular, and auricular branches. This nerve conveys sensations from the mucosa of the middle ear, auditory tube, and mastoid air cells to the spinal trigeminal nucleus. Visceral afferent fibers within the carotid sinus department set up synaptic connections through interneurons within the reticular formation of the medulla with the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus and, concurrently, with the neurons of the reticulospinal tracts. In flip, the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus sends preganglionic parasympathetic fibers to the cardiac plexus, decreasing cardiac contractility (negative chronotropic effect) whereas the medullary reticulospinal tract inhibits or reduces the firing rate of the preganglionic sympathetic neurons that supply the cardiac plexus and the cutaneous arterioles. The lower within the sympathetic output combined with the vagal inhibition results in a decrease of cardiac rate and output. The decrease in the peripheral vascular resistance results in a lower in blood strain.
Purchase arzomicin us
Caution her to not discon tinue drug or change dosage unless instructed by prescriber. In addition, as a end result of insulin and glucagon ranges happen in an inverse relationship to plasma glucose stage, increased insulin degree will lower glucagon stage, which inhibits glucagon stimulation of the liver that increases plasma glucose stage. Although its exact mechanism is unclear, liraglutide additionally delays gastric emptying, which helps stop a sudden rise in plasma glucose level after eating. If any hypersensitivity reaction occurs, discontinue liraglutide and notify the prescriber. Report persistent extreme belly ache; it could radiate to the again and may be accompanied by vomiting. Report any episode of hypoglycemia as a result of dosage of other antidiabetic may need adjustment. Treat hypoglycemia with a glucosecontaining meals or beverage, or give glucagons, as ordered, to raise blood glucose degree. Tell patient to inject drug into his stomach, thigh, or higher arm and to rotate websites to reduce injectionsite reactions. Initial: 30 mg once daily in the morning, elevated as wanted in increments of 10 or 20 mg every day every wk. The drug additionally releases and blocks reuptake of dopamine in limbic regions of mind. Reassure patient that signs and symptoms typically improve after the dose is decreased or drug is discontinued. Take seizure precautions in all patients, and notify prescriber if a seizure happens. If systolic blood stress falls to a hundred mm Hg or less during remedy, upkeep dosage decreased to 2. Decreased release of aldosterone reduces sodium and water reabsorption and will increase their excretion, thereby decreasing blood stress. Anaphylaxis has additionally occurred with some sufferers present process lowdensity lipoprotein apheresis with dextran sulfate absorption. If patient develops jaundice or a marked elevation in liver enzyme levels, withhold drug and notify prescriber. Onset 1�3 wk Peak Duration Unknown Unknown Mechanism of Action lithium citrate Cibalith-S Class and Category Chemical class: Alkaline steel, monovalent cation Therapeutic class: Antidepressant, antimanic Pregnancy class: D To deal with recurrent bipolar affective capsules, tablets May improve presynaptic degradation of the catecholamine neurotransmitters serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine; inhibit their launch at neuronal synapses; and decrease postsynaptic receptor sensitivity. These actions might appropriate overactive catecholamine techniques in patients with mania. Indications and Dosages Contraindications disorder, to stop bipolar dysfunction depression Adults and children age 12 and over. Even a barely excessive blood level is dangerous, and some patients show signs of toxicity at normal ranges. Know that Brugada syndrome is a dysfunction in which electrocardiographic abnormalities occur and can lead to sudden demise. Patients in danger embrace those with a family history of Brugada syndrome or a household history of sudden death before the age of forty five years. By inhibiting this enzyme, lomefloxacin interferes with bacterial cell replication and causes cell demise. Contraindications History of tendinitis or tendon rupture, hypersensitivity to lomefloxacin or any quinolone derivative Indications and Dosages Interactions medicine tablets respiratory tract infections attributable to prone organisms, together with Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis To deal with uncomplicated cystitis brought on by Adults. Escherichia coli; to treat uncomplicated cystitis caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, or Staphylococcus saprophyticus aluminum-, calcium-, or magnesiumcontaining antacids; iron salts; sucralfate; zinc: Decreased absorption and blood level of lomefloxacin cyclosporine: Possibly elevated blood cyclosporine stage, elevated nephrotoxicity probenecid: Decreased lomefloxacin excretion, increased risk of toxicity warfarin: Possibly elevated anticoagulant effect and risk of bleeding 692 lomitapide mesylate of peripheral neuropathy (pain, burning, tingling, numbness, weak spot, or adjustments in sensations of sunshine contact, pain, temperature, place, or vibration) to prevent an irreversible condition or tendon rupture that requires quick rest and avoidance of exercise involving affected area. Urge patient to cease drug and notify prescriber at first sign of photosensitivity, corresponding to pores and skin burning, redness, swelling, blisters, rash, itching, or dermatitis. Tell patient to stop lomefloxacin and notify prescriber if rash or different allergic response develops. Initial: 5 mg as soon as daily with full glass of water 2 hrs after evening meal with dosage increased to 10 mg as soon as day by day after 2wks, as needed. Dosage additional elevated in four wk increments to 20 mg as quickly as every day, then to forty mgs as soon as day by day to 60 mg once every day, as needed. For sufferers who develop elevated transaminases three times or greater however less than 5 occasions higher regular limits throughout therapy, every day dosage decreased with degree of reduction individualized.
Arzomicin 250 mg without a prescription
The solution ought to be stored within the refrigerator shielded from direct daylight, if not used instantly. Notify prescriber instantly if a reaction happens, as a outcome of death has occurred with some sufferers experiencing hypersensitivity reactions. Expect to provide emergency medical treatment as ordered and indicated by severity of response. Also avoid high doses in hiatal hernia and reflux esophagitis as a outcome of they could aggravate esophagitis. [newline]Elderly sufferers are extra sensitive to the effects of the drug, even small doses, and are extra probably to develop adverse reactions. Onset 1 hr Peak 2�4 hr Duration 24 hr Mechanism of Action � Instruct patient to take belladonna alkaloids 30 to 60 minutes before consuming. This decreases aldosterone secretion, slightly growing serum potassium stage and fluid loss. Assess affected person routinely for indicators and signs of liver dysfunction, such as jaundice and fatigue. Notify prescriber if affected person develops jaundice or displays elevated liver enzyme ranges, as drug will need to be discontinued. If it extends to larynx and affected person has laryngeal stridor or indicators of airway obstruction, put together to give epinephrine subcutaneously immediately, as prescribed, and discontinue benazepril. Be aware that black patients have a better incidence of angioedema compared to nonblacks. If cough turns into bothersome or interferes with sleep or activities, patient ought to notify prescriber. Releasing drug in the mouth could anesthetize mouth and throat, inflicting threat of choking. B benzonatate Benzonatate Softgels, Tessalon Perles Class and Category Chemical class: Para-aminobenzoic acid (tetracaine-like) Therapeutic class: Nonnarcotic antitussive Pregnancy class: C Indications and Dosages To relieve cough capsules, perles Adults and youngsters over age 10. Peak Duration 15�20 min Unknown 3�8 hr Mechanism of Action Anesthetizes stretch receptors in respiratory tract, lung tissue, and pleura, interfering with their exercise and decreasing cough reflex at its source. M Onset 1�2 hr 15 min Peak Duration Unknown 24 hr Unknown 24 hr Mechanism of Action � Advise patient to stay in bed and call for assistance to cut back risk of damage. If patient has elevated salivary secretions, anticipate to administer benztropine after meals. Onset Peak Duration Unknown Unknown eight days Mechanism of Action Inhibits calcium motion into coronary and vascular smooth-muscle cells by blocking gradual calcium channels in their membranes. This decreases intracellular calcium stage, which inhibits smoothmuscle cell contractions and causes: � leisure of coronary and vascular clean muscle tissue, decreased peripheral vascular resistance, and decreased systolic and diastolic blood stress, which decrease myocardial oxygen demand � depression of impulse formation (automaticity) and conduction velocity. Instead, gradually taper dosage as prescribed to prevent increased frequency and length of chest pain as increased calcium strikes into cells, causing coronary artery spasm. Especially notice decreased potassium stage, which can worsen present arrhythmias or induce new ones. Binds to intracellular glucocorticoid receptors and suppresses inflammatory and immune responses by: � inhibiting neutrophil and monocyte accumulation at inflammation website and suppressing their phagocytic and bactericidal activity � stabilizing lysosomal membranes � suppressing antigen response of macrophages and helper T cells � inhibiting synthesis of inflammatory response mediators, such as cytokines, interleukins, and prostaglandins. For intra-arterial or intrasynovial injection; 1 week for intralesional injection in soft tissue. Use betamethasone cautiously in patients with ocular herpes simplex as a end result of corneal perforation could occur. Because drug might cause immunosuppression, new an infection might develop during remedy. Sodium and water retention and potassium and calcium depletion might occur with high-dose betamethasone remedy. If so, expect to limit sodium intake and supply potassium and calcium supplements. To prevent muscle atrophy, avoid subcutaneous injection, injection in deltoid website, and repeated I. If patient additionally develops fever and malaise, suspect septic arthritis and notify prescriber instantly. B betaxolol hydrochloride Kerlone Class and Category Chemical class: Selective beta1-adrenergic blocker Therapeutic class: Antihypertensive Pregnancy class: C Indications and Dosages To treat hypertension alone or with different antihypertensives tablets Adults.
250mg arzomicin for sale
Loading: 15 to 25 mcg/kg in three or extra divided doses, with first dose equal to 50% of whole dose. Loading: 10 to 15 mcg/kg whole dose given in three divided doses every 6 to 8 hr, with first dose equal to 50% of whole dose. Loading: 10 to 15 mcg/kg complete given in 3 divided doses each 6 to 8 hr, with first dose equal to 50% of total dose. The drug can be not really helpful in patients with idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis as a outcome of outflow obstruction could worsen due to the inotropic results of digoxin. If they seem, notify prescriber, examine serum digoxin level as ordered, and expect to withhold drug till degree is known. Elderly patients, especially these with coronary insufficiency, are more vulnerable to arrhythmias-particularly ventricular fibrillation-if digitalis toxicity happens. Also monitor potassium level usually when giving potassium salts because hyperkalemia in patients receiving digoxin could be deadly. Warn about attainable toxicity from taking an extreme amount of and decreased effectiveness from taking too little. Urge her to notify prescriber if pulse falls below 60 beats/minute or suddenly increases. Caution against carrying digoxin in something aside from its authentic labeled container. D digoxin immuneFab (ovine) Digibind Class and Category Chemical class: Digoxin-specific antigenbinding fragments Therapeutic class: Digitalis glycoside antidote Pregnancy category: C 360 digoxin immuneFab (ovine) Other: Allergic response (difficulty respiratory, urticaria), febrile reaction, hypokalemia � Expect every 38-mg vial of purified digoxin immune Fab to bind about 0. For very small doses, reconstituted 38-mg vial may be diluted with 34 ml of regular saline answer to yield 1 mg/ml. If take a look at causes a systemic reaction, apply tourniquet above test site, notify prescriber, and put together to reply to anaphylaxis. Indications and Dosages To deal with acute toxicity from a identified quantity of digoxin elixir or tablets i. Individualized dosage for digoxin toxicity: dose (mg) 5 serum digoxin degree (ng/ml) multiplied by body weight (kg), then divided by 100, after which multiplied by 38. Individualized dosage for digitoxin toxicity: dose (mg) 5 serum digitoxin degree (ng/ml) multiplied by body weight (kg) after which divided by 1,000, multiplied by 38, and rounded as a lot as next entire vial. Peak Duration 15�30 min Unknown 8�12 hr Mechanism of Action Binds with digoxin or digitoxin molecules. As the free serum digoxin stage declines, tissue-bound digoxin enters the serum and also is bound and excreted. At therapeutic doses, it inhibits norepinephrine reuptake, increasing vasoconstriction. Drug constricts veins greater than arteries, growing venous return whereas reducing venous stasis and pooling. After giving nasal dihydroergotamine, monitor patient for signs of widespread blood vessel constriction and antagonistic reactions caused by decreased circulation to many physique areas. Indications and Dosages tetany To treat hypoparathyroidism capsules, oral answer, tablets Adults and adolescents. Initial: 1 to 5 mg day by day for 4 days; then continued or decreased to one-quarter the dose. Peak Duration Several hr Unknown Up to 9 wk Mechanism of Action Stimulates intestinal calcium absorption and mobilizes bone calcium when parathyroid hormone and renal tissue fail to elevate the serum calcium level. Delayed therapy can lead to death from cardiac and renal failure brought on by widespread calcification of sentimental tissues, together with the heart, blood vessels, kidneys, and lungs. Place affected person on bed rest, administer fluids and a laxative, and give low-calcium diet as ordered. Initial: 30 mg 3 times daily or 4 times day by day earlier than meals and at bedtime, increased every 1 or 2 days as acceptable. Then 10 mg/hr for continued reduction of heart fee after bolus, elevated by 5 mg/hr, as needed.
Tofu (Soy). Arzomicin.
- What is Soy?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Heart disease.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Reducing the risk of developing breast cancer.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96936
Cheap arzomicin
Discourage hazardous actions, corresponding to driving, until results of drug are recognized. If response is inadequate, dosage increased to 5 mg and then 10 mg day by day, as wanted. Unknown Peak Duration 1�3 hr Unknown May cut back blood pressure by competing with betaadrenergic receptor agonists, which helps reduce cardiac output, lower sympathetic outflow to peripheral blood vessels, and inhibit renin. It also can intrude with endogenous insulin release in response to hyperglycemia, requiring adjustment of oral antidiabetic dosage. Reduces cardiac output and tachycardia, causes vasodilation, and decreases peripheral vascular resistance, which reduces blood strain and cardiac workload. Maximum (for sufferers with delicate to moderate coronary heart failure): 50 mg twice day by day if patient weighs greater than 85 kg (187 lb). Increased again as wanted each three to 10 days till reaching tolerance or goal dose of 80 mg once daily. For affected person with coronary heart rate below fifty five beats/min, extendedrelease dosage decreased as scientific situation indicates. In patients with diabetes mellitus it may masks indicators of hypoglycemia, corresponding to tachycardia, and may delay restoration. If swallowing capsules is troublesome, tell patient he could open capsule and sprinkle beads on a spoonful of cold applesauce after which eat the applesauce immediately with out chewing. C caspofungin acetate Cancidas Class and Category Chemical class: Echinocandins Therapeutic class: Antifungal Pregnancy class: C To treat invasive aspergillosis in patients Indications and Dosages i. Initial: 70 mg on day 1, adopted by 50 mg daily for a minimum of 14 days, including no much less than 7 days after neutropenia and symptoms have resolved. Fungal cell exterior Inhibited (1,3)-D-glucan (1,3)-D-glucan Caspofungin Mechanism of Action Caspofungin acetate interferes with fungal cell membrane synthesis by inhibiting the synthesis of (1, 3)Dglucan. A polypeptide, (1, 3)Dglucan is the essential element of the fungal cell membrane that makes it inflexible and protecting. This mechanism of motion is most effective towards vulnerable filamentous fungi, similar to Aspergillus. Initial: 70 mg/m2 on day 1, adopted by 50 mg/m2 day by day for at least 14 days, including a minimal of 7 days after neutropenia and signs have resolved. Contraindications Interactions medicine Hypersensitivity to caspofungin acetate or its components carbamazepine, dexamethasone, efavirenz, nelfinavir, nevirapine, phenytoin, rifampin: cefaclor � To prepare 70mg loading dose, let vial reach room temperature. Dilute for admin istration by transferring 10 ml of reconstituted drug to 250 ml normal saline resolution. Dilute for admin istration by transferring only 10 ml of reconstituted drug to 250 ml regular saline resolution. To dilute, switch only 7 ml of reconstituted drug to 250 ml normal saline answer or, if wanted, to a hundred ml regular saline answer. Report these symptoms immediately and count on caspofungin remedy to be discontinued. For severe infections, corresponding to pneumonia, or those brought on by less susceptible organisms, 500 mg each eight hr. For otitis media and pharyngitis, complete every day dosage divided and given every 12 hr, if wanted. Interferes with bacterial cell wall synthesis by inhibiting crosslinking of peptidoglycan strands, which stiffen cell membranes. Children: For delicate to moderate infections, 25 to 50 mg/kg daily divided equally and given three times day by day or four occasions day by day; for extreme infections, 100 mg/kg every day divided equally and given three times day by day or four instances every day. Dosage reduced to 60% and given each 12 hr for youngsters with creatinine clearance of 40 to 70 ml/min/1. Mechanism of Action Interferes with bacterial cell wall synthesis by inhibiting the ultimate step in the crosslinking of peptidoglycan strands. Also use cautiously in sufferers hypersensitive to penicillin as a end result of crosssensitivity has occurred in about 10% of such patients. Inject slowly Nursing Considerations over three to 5 minutes by way of tubing of a flowing suitable I. To deal with acute bacterial otitis media To deal with pharyngitis or tonsillitis brought on Adults and adolescents.
Purchase arzomicin canada
She also needs to avoid scorching baths or sunbathing because elevated physique temperature might enhance fentanyl launch, leading to a possible overdose. If she develops a fever or becomes overheated from strenuous exercise whereas sporting a patch, she should contact the prescriber immediately. To use, insert the nozzle of the Lazanda bottle a short distance (about half of inch or 1 cm) into the nose and level in path of the bridge of the nostril, tilting the bottle barely. Have patient press down firmly on the finger grips till he hears a "click" and the number in the counting window advances by 1. Instruct him to spray the contents of the unit into his mouth rigorously, underneath his tongue. For buccal tablets, patient should flush leftover drug down the toilet when now not wanted. For sublingual spray, remind patient to dispose of any used or unneeded items instantly in the disposal bottle supplied with each allotted carton. If accidental exposure happens, the person should remove the patch, wash the area well with water, and seek medical attention. Up to 6 mg/kg elemental iron daily in divided doses 3 times day by day or 4 times day by day for 4 to 6 mo. To present iron supplementation throughout caplets, capsules, chewable tablets, dried capsules, dried. Iron is a vital part of hemoglobin, myoglobin, and several enzymes, together with cytochromes, catalase, and peroxidase. When administering as a gradual intravenous push, give at the fee of about a hundred mg (2 ml) per minute. When administering through infusion, dilute up to 750 mg of iron in no more than 250 ml of sterile zero. If current, discontinue drug instantly, notify prescriber, and be prepared to provide supportive care, as wanted. E F 492 ferumoxytol iron by dropper, direct her to place drops well back on the tongue and to comply with with water or juice. Tell her that iron stains may be removed by brushing with baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) or medicinal peroxide (hydrogen peroxide 3%). In case of iron toxicity or unintentional iron overdose (a leading explanation for fatal poisoning in kids beneath age 6), give deferoxamine, as prescribed. If affected person should take liquid Indications and Dosages To deal with iron deficiency anemia in sufferers with continual kidney illness i. Mechanism of Action Isolates the bioactive iron from plasma parts till the iron-carbohydrate complicated enters the reticuloendothelial system macrophages of the liver, spleen, and bone marrow. The iron is released from the iron-carbohydrate complicated inside vesicles in the macrophages. Expect to readminister the drug in sufferers with persistent or recurrent iron deficiency anemia. Provide supportive care, as indicated, by severity of reaction and count on drug to be discontinued. Onset Unknown Peak 5 hr Duration Unknown Mechanism of Action Exerts antimuscarinic (atropine-like) and potent direct antispasmodic (papaverinelike) actions on smooth muscle in the bladder. Fesoterodine has an lively metabolite that inhibits bladder contraction and reduces detrussor strain. If current, notify prescriber, as dosage could need to be lowered or drug discontinued. Nursing Considerations � Use cautiously in sufferers with vital bladder outlet obstruction as a end result of fesoterodine could cause urine retention. If present, discontinue fesoterodine therapy instantly, as ordered, and provide emergency supportive care, including maintaining a patent airway, as needed. If a extreme response happens, discontinue fidaxomicin immediately and notify prescriber.
Order arzomicin with mastercard
A medical and experimental examine on all-trans retinoic acid-treated acute promyelocytic leukemia patients. Treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia with all-trans retinoic acid: an update of the New York expertise. Biological implications of consistent chromosome rearrangements in leukemia and lymphoma. Clinical and biologic hallmarks of the Philadelphia chromosome in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Altered transcription of the c-abl oncogene in K562 and different persistent myelogenous leukemia cells. The human mobile abl gene product in the continual myelogenous leukemia cell line K562 has an related tyrosine protein kinase activity. An alteration of the human c-abl protein in K562 leukemia cells unmasks related tyrosine kinase activity. A novel abl protein expressed in Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. A novel c-abl protein product in Philadelphia-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Chromosomal abnormalities determine high-risk and low-risk patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Philadelphia chromosome and terminal transferase-positive acute leukemia: similarity of terminal section of persistent myelogenous leukemia and de novo acute presentation. Bcr-Abl kinase domain mutations, drug resistance, and the road to a remedy for continual myeloid leukemia. Recent advances within the remedy of Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Erythroleukemia induction by Friend murine leukemia virus: insertional activation of a model new member of the ets gene household, Fli-1, closely linked to c-ets-1. The Ewing household of tumors-a subgroup of small-round-cell tumors outlined by specific chimeric transcripts. Chromosomal sublocalization of the two;13 translocation breakpoint in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Pax-3 is required for the development of limb muscular tissues: a possible function for the migration of dermomyotomal muscle progenitor cells. Synovial sarcoma: a retrospective analysis of 271 sufferers of all ages handled at a single establishment. Association between an oncogene and an anti-oncogene: the adenovirus E1A proteins bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Abnormalities in structure and expression of the retinoblastoma gene in small cell lung cancer cell strains and xenografts in nude mice. Homozygous deletion of the retinoblastoma gene in an acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T) cell line. The retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product: a attribute sample in normal cells and abnormal expression in malignant cells. Frequent inactivation of the retinoblastoma anti-oncogene is restricted to a subset of human tumor cells. At least 4 totally different chromosomal areas are involved in loss of heterozygosity in human breast carcinoma. Detection of frequent p53 gene mutations in main gastric most cancers by cell sorting and polymerase chain reaction single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis. Selective G to T mutations of p53 gene in hepatocellular carcinoma from southern Africa [see comments]. Status of c-myc, p53 and retinoblastoma genes in human papillomavirus optimistic and adverse squamous cell carcinomas of the anus. Linear development in kids with acute lymphoblastic leukemia handled with out cranial irradiation. Wild-type p53 suppresses development of human prostate cancer cells containing mutant p53 alleles.
Order generic arzomicin from india
Children, adolescents, and patients with rheumatoid arthritis, especially these with very active illness, are at best risk. Dissolved powder may be stored in fridge for up to 6 hours after mixing and then must be discarded. Tell him to seek medical attention promptly for any suspicious indicators and signs. Dose repeated in 2 to four hr, if wanted, then each four to 6 hr based mostly on patient response. These inhibitory results improve urinary excretion of sodium, chloride, and water, causing profound diuresis. Drug also increases the excretion of potassium, hydrogen, calcium, magnesium, bicarbonate, ammonium, and phosphate. If affected person receives once-daily dosing, advise him to take the dose in the morning to keep away from sleep disturbance attributable to nocturia. Contraindications Hypersensitivity to ethambutol or its elements, inability to report adjustments in vision, optic neuritis Interactions drugs antacids that contain aluminum hydroxide: Decreased absorption of ethambutol different neurotoxic medicine: Increased risk of neurotoxicity, corresponding to optic and peripheral neuritis affected person teaching prescriber immediately if affected person develops vision changes, and anticipate ethambutol to be stopped if they happen. This is especially likely if therapy is extended or dosage exceeds 15 mg/kg every day. Indications and Dosages To present short-term reduction from insomnia ethionamide capsules 457 Adults. Peak Duration 15�60 min Unknown 5 hr Mechanism of Action Exerts sedative-hypnotic, muscle relaxant, and anticonvulsant results possibly by depressing the reticular activating system. If affected person has received prolonged therapy, anticipate to discontinue drug progressively to stop withdrawal signs. Notify prescriber when you detect proof of withdrawal, corresponding to diaphoresis, hallucinations, irritability, muscle twitching, nausea, nervousness, restlessness, seizures, sleep disturbance, tremor, vomiting, and weakness. Mechanism of Action May inhibit peptide synthesis, leading to bacteriostatic motion in opposition to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Maintenance: Increased by 250 mg every four to 7 days till management is achieved with minimal opposed reactions. Initial: Up to 750 mg daily, based on weight and age, in four to 6 divided doses, adjusted as wanted and tolerated. Limits the spread of seizure activity and the start of latest seizures by: � regulating voltage-dependent sodium and calcium channels in neurons � inhibiting calcium motion throughout neuronal membranes tablets complex partial seizures as preliminary or adjunct remedy, or when different medicine are ineffective Mechanism of Action 460 ethotoin molindone: Possibly lowered seizure threshold and impaired absorption and decreased therapeutic results of ethotoin oral anticoagulants: Possibly impaired metabolism of those medicine and increased danger of ethotoin toxicity; presumably elevated anticoagulant impact initially, but decreased effect with extended remedy oral contraceptives that comprise estrogen and progestin: Possibly breakthrough bleeding and decreased contraceptive effectiveness rifampin: Possibly decreased therapeutic effects of ethotoin streptozocin: Possibly decreased therapeutic effects of streptozocin sucralfate: Possibly decreased ethotoin absorption tricyclic antidepressants: Possibly lowered seizure threshold and decreased therapeutic results of ethotoin; probably decreased blood stage of tricyclic antidepressants valproic acid: Possibly decreased ethotoin degree, elevated valproic acid level vitamin D analogues: Decreased vitamin D analogue exercise; threat of anticonvulsantinduced rickets and osteomalacia xanthines: Possibly inhibited ethotoin absorption and elevated clearance of xanthines � enhancing sodium-potassium adenosine triphosphatase exercise in neurons and glial cells. Plan to cut back dosage etidronate disodium progressively or substitute one other drug, as prescribed. Explain that this registry is collecting information about the protection of antiepileptic medication throughout pregnancy. To prevent and deal with heterotopic tablets ossification after complete hip substitute To forestall and deal with heterotopic tablets Adults. Oral etidronate may begin at 20 mg/kg/day for 30 days on the day after final infusion. Mechanism of Action Inhibits regular and abnormal bone resorption by reducing bone turnover and 462 etidronate disodium � Give parenteral kind slowly over a minimum of 2 hours. It additionally inhibits the abnormal bone resorption that will occur with cancer and reduces the amount of calcium that enters the blood from resorbed bone. Urge him to drink a full glass of water with tablets and to keep away from taking drug with milk or other high-calcium foods. Maximum: 1,200 mg daily for patients weighing 60 kg (132 lb) or more; 20 mg/kg daily for those less than 60 kg. Maximum: 1,200 mg daily for patients weighing 60 kg or extra; 20 mg/ kg/day for patients weighing less than 60 kg. Onset 30 min Peak 1�2 hr Duration 4�12 hr Adverse Reactions Mechanism of Action Blocks the activity of cyclooxygenase, the enzyme needed for prostaglandin synthesis. Prostaglandins, important mediators of the inflammatory response, trigger native vasodilation with swelling and pain. Rarely, elevated ranges may progress to extreme hepatic reactions, including fatal hepatitis, hepatic necrosis, and hepatic failure.
Real Experiences: Customer Reviews on Arzomicin
Wenzel, 51 years: The adjustments in near vision happen when the eyeball has a traditional anteroposterior dimension and functional refractive media inside regular vary.
Hanson, 58 years: Changes in aminoacidergic and monoaminergic neurotransmission in the hippocampus and amygdala of rats after ayahuasca ingestion.
Tangach, 57 years: If a couple of subcutaneous injection is required, administer the injections at different sites on the physique.
Rune, 23 years: As adjunct to treat edema attributable to oral solution, tablets cirrhosis, corticosteroids, estrogen, heart failure, or renal problems Adults.
8 of 10 - Review by O. Ines
Votes: 93 votes
Total customer reviews: 93
References
- Canto MT, Devesa SS. Oral cavity and pharynx cancer incidence rates in the United States, 1975-1998.
- Swanson RS. Is an FDG-PET scan the new imaging standard for colon cancer? Ann Surg Oncol 2001;8(10):752- 753.
- Chandradeva K, Palin C, Ghosh SM, et al: Percutaneous transtracheal jet ventilation as a guide to tracheal intubation in severe upper airway obstruction from supraglottic oedema. Br J Anaesth 94:683, 2005.
- O'Brien S, del Giglio A, Keating M. Advances in the biology and treatment of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1995;85(2):307-318.