Doxepin dosages: 75 mg, 25 mg, 10 mg
Doxepin packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills, 120 pills

Generic 75 mg doxepin overnight delivery
The most essential neurologic indicators and symptoms that accompany basilar artery occlusion are: 1. Limb paralysis is often bilateral however typically uneven; stiffness, hyperreflexia, and extensor plantar reflexes are discovered when inspecting the weak limbs. Some sufferers present with a hemiparesis, but examination exhibits weak point and reflex adjustments within the contralateral limbs. Infarction could have an effect on cranial motor nuclei, causing paralysis of the face, palate, pharynx, neck, or tongue on one or each side. The 9th- to 12th-nerve nuclei are positioned within the medullary tegmentum, which is usually under the level of infarction. Weakness of the cranial musculature innervated by these nuclei causes dysarthria, dysphonia, hoarseness, dysphagia, and tongue weakness. Clot additionally could extend to block anterior spinal artery department, inflicting hemiplegia, or embolization to basilar bifurcation might trigger "high of basilar" syndrome. The ensuing weak point is referred to as pseudobulbar because it entails the descending pathways controlling the bulbar nuclei rather than the nuclei themselves. Exaggerated jaw and facial reflexes, increased gag reflex, and easily induced emotional incontinence with excessive laughing and/or crying are found. Such sufferers have been referred to as having the locked-in syndrome because of their loss of motor operate. Nystagmus: the vestibular nuclei and their connections are also often affected, inflicting vertical and horizontal nystagmus. When the reticular formation is affected bilaterally within the medial pontine tegmentum, coma results. Sensory and cerebellar abnormalities are absent or slight because the infarct normally impacts the midline and paramedian buildings within the foundation pontis, sparing the spinothalamic tracts and the cerebellum. Collateral circulation is principally through the circumferential vessels, which course across the lateral parts of the brainstem to nourish the lateral base, tegmentum, and cerebellum. Emboli small enough to cross via the vertebral arteries seldom lodge in the proximal basilar artery, a vessel larger than every intracranial vertebral artery, but reach the distal basilar artery or its terminal branches. The distal basilar artery supplies the midbrain and diencephalon by way of small vessels that pierce the posterior perforated substance. The lesion often interrupts the afferent reflex arc by interfering with fibers going toward the Edinger-Westphal nucleus. The third-nerve nucleus may also be concerned, as nicely as the rostral descending sympathetic system. Decreased pupillary reactivity and eccentricity or an oval shape of the pupil can be discovered. The adduction vector neutralizes the kidnapping movement, and so abduction is incomplete. Hypersomnolence or frank coma can result from bilateral paramedian rostral brainstem dysfunction. Patients are unable to form new reminiscences and will not be in a position to recall events simply previous their stroke. There usually are different behavioral abnormalities, together with agitation, hallucinations, and abnormalities that mimic lesions of the frontal lobe. The tuberothalamic (polar) artery arises on both sides from the middle third of the posterior communicating artery and provides the anteromedial and anterolateral thalamic nuclei. Unilateral anterolateral thalamic infarction in the distribution of the polar artery on either aspect usually causes abulia, facial asymmetry, transient minor contralateral motor abnormalities and, at instances, aphasia (left lesions) or visual neglect (right lesions). Abulia, with slowness, decreased quantity of activity and speech, and lengthy delays in responding to queries or dialog, is the predominant abnormality. The thalamic-subthalamic arteries (also called thalamoperforating) originate from the proximal posterior cerebral arteries and provide essentially the most posteromedial portion of the thalamus close to the posterior commissure. The right- and left-sided arteries usually arise individually but can originate from a single unilateral artery or a typical pedicle. Unilateral lesions are usually characterized by paresis of vertical gaze (upward or each upward and downward) and by amnesia.
Purchase doxepin mastercard
Some patients also show distinguished psychomotor disturbances, including catatonia. Together, these florid and infrequently dramatic symptoms are referred to as positive symptoms and contrasted with unfavorable and cognitive symptoms, the latter being answerable for much of the disability that characterizes schizophrenia. Negative signs are categorized right into a reduced emotional expressivity cluster (restricted or flat affect) and an avolition/apathy/ anhedonia cluster. Many schizophrenia sufferers battle with cognitive impairment in the realms of working reminiscence, attention/vigilance, verbal studying and reminiscence, visible studying and memory, reasoning and problem solving, velocity of processing, and social cognition. However, if temper symptoms dominate the general course of a psychotic illness, a prognosis of schizoaffective dysfunction could be given. Schizophrenia is a analysis of exclusion; various avenue drug utilization, drugs, and medical causes of psychosis must initially be excluded earlier than prognosis as a end result of these can mimic the core symptoms of schizophrenia. Many patients with schizophrenia experience symptoms that in hindsight are acknowledged as a prodrome earlier than the onset of their florid psychosis. Unspecific prodromal signs (anxiety, despair, social withdrawal) ultimately give rise to attenuated psychotic symptoms before schizophrenia declares itself by the onset of psychosis. Because schizophrenia is a syndrome, not all sufferers experience signs from all domains. Schizophrenia can be characterized by a fluctuating illness course, the place intervals of exacerbation with distinguished psychosis alternate with intervals of remission. The typical age at onset is between 15 and 30 years, with onset after age forty five years being uncommon. Patients with schizophrenia usually die many years earlier than individuals within the general population. Its extra medical mortality is partly preventable because modifiable danger components. Other necessary danger elements for schizophrenia embody in utero insults throughout mind improvement, such as publicity to infections; obstetric complications; superior paternal age; social components, corresponding to urbanicity or immigration standing; and early heavy hashish use. The neuropathology and pathophysiology of the network dysfunction in schizophrenia remain to be resolved. Critical brain regions involved embrace frontal cortical areas, notably dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, the thalamus, and numerous limbic and dopaminergic midbrain areas. Schizophrenia may be considered as a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects mind circuits and develops in levels. Alternatively, she may have significant negative symptoms, including anhedonia, amotivation, and poverty of speech. Therefore prevention of this extreme end result requires therapy of goal patients at earlier levels. After resolution of the preliminary psychosis, most sufferers require upkeep remedy with an antipsychotic medicine to cut back the likelihood of a psychotic relapse. Despite nice differences in particular person receptor pharmacologic sites of exercise, at present available antipsychotics are equally effective and differ mostly in their propensity towards unwanted effects. Only clozapine is shown to be more practical in treatment-refractory sufferers with schizophrenia. Problematic long-term side effects of all antipsychotics include tardive dyskinesia and the metabolic syndrome. Negative and cognitive signs, particularly, show little enchancment with antipsychotics alone. Instead, the great remedy of schizophrenia requires integration of pharmacologic treatment with psychologic therapies and concomitant psychosocial rehabilitation. The availability of cognitive-behavioral remedy and cognitive remediation with rehabilitation holds promise for treating persistent signs and cognitive deficits. To normalize these tips, a "normal drink" is defined as an ethanol alcohol content of 14 grams (equivalent to 12 ounces of beer, 5 ounces of desk wine, or 1. It is taken into account "low-risk" for healthy grownup males under age sixty five years to consume not more than 14 standard drinks per week, with up to 4 drinks per day, and for healthy grownup nonpregnant ladies beneath age 65 years and healthy men and women age sixty five years and older, no more than 7 standard drinks per week and up to 3 standard drinks per day.
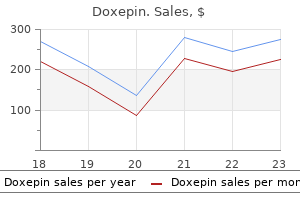
Order discount doxepin line
Radiation-induced meningiomas are inclined to have a better frequency of multiplicity and higher fee of malignancy than sporadic meningiomas. These are additional subdivided based on their morphology into meningotheliomatous (including "psammomatous" tumors with attribute whorl patterns of cells), fibromatous, and angioblastic types. Treatment approaches for all of these subtypes of benign meningiomas are the identical. These are characterized by greater mitotic activity, defined as having greater than or equal to 4 mitoses per high-powered subject, and three or more of the next options: increased cellularity, high nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio, outstanding nucleoli, uninterrupted sheetlike growth, or areas of necrosis. Presenting indicators and symptoms rely upon the situation and progress fee of the tumor. Because most meningiomas are slow growing, patients are frequently asymptomatic, with the invention of the tumor an incidental finding. Any signs or signs that do develop are usually secondary to compression of underlying constructions. Seizures are sometimes presenting signs of meningiomas, especially those positioned close to cerebral cortex. Focal weakness is one other frequent complaint, with the sample of weak spot a potential clue as to the location of the tumor. For example, bilateral lower extremity weak spot in the absence of a spinal twine lesion can typically be seen with parasagittal lesions arising from the falx and compressing the adjoining motor strips of each Meningioma histopathology Cerebral vessels on floor Superior view of brain. A potential concern with these lesions is involvement of the sagittal sinus, which can lead to venous infarction. Spinal meningiomas can also trigger bilateral leg weakness, but that is typically accompanied by numbness. Foramen magnum meningiomas can present with insidious weakness of the arm and leg, which progresses to contain the contralateral limbs. This is accompanied by neck pain, worsened with neck flexion or Valsalva maneuvers. Because of the subtly progressive symptoms, this may be hard to diagnose and may be confused with a quantity of sclerosis. Finally, meningiomas can come up from the optic sheath, leading to slowly progressive loss of vision. Other indicators and signs include ataxia and hemiparesis secondary to lesions within the posterior fossa, inflicting brainstem compression. Meningiomas arising at the cerebellopontine angle can produce sensorineural listening to loss. Occasionally, they are often quite adherent to adjacent cranial nerves and vasculature, rendering them tough to remove. Because the vast majority of meningiomas are very slowly growing, the brain has time to adapt to the enlarging mass. Thus tumors in the frontal or occipital lobe can turn into fairly large earlier than the tenuous strain relationships decompensate, leading to symptomatic presentation. Those tumors arising within the frontal lobe could current with cognitive or persona adjustments or different mental standing changes. Typically, meningiomas are isointense to hypointense on T1 and isointense to hyperintense on T2, with robust homogeneous enhancement. Although bony involvement from cerebral convexity tumors is uncommon, virtually 50% of skull base tumors may have secondary involvement of the bone. It is affordable to comply with these patients conservatively with lively surveillance, withholding therapy until the tumor turns into symptomatic or will increase in dimension considerably. This is especially true for aged patients (older than 70 years) or those with multiple surgical comorbidities. In patients with symptomatic lesions or asymptomatic tumors that appear to be infiltrative or related to vasogenic edema, surgical resection is really helpful. In these instances, adjuvant radiotherapy ought to be thought of as a end result of retrospective studies have reported improved progression free survival, although not total survival. Radiotherapy alone may be efficient for these lesions which might be surgically inaccessible with native management rates of greater than 90% in 5 years. Despite the shortage of huge prospective trials, adjuvant radiotherapy is beneficial for incompletely resected tumors. Patients usually present with quite a lot of neurologic and endocrinologic abnormalities, depending on the tumor type and growth traits. Although the pituitary adenoma is the most common sellar tumor, other tumor varieties exist, including pituitary carcinomas, craniopharyngiomas, and Rathke cleft cysts.
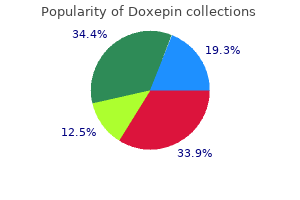
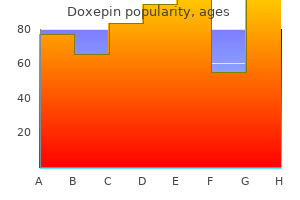
75 mg doxepin with amex
Alternatively, monodeiodination of the inside ring yields reverse T3, which is biologically inactive. Proportioning of T4 between T3 and reverse T3 regulates the supply of active thyroid hormone. Thyroid hormone is a serious optimistic regulator of the basal metabolic fee and thermogenesis. Other essential actions of thyroid hormone are elevated coronary heart fee, cardiac output, and air flow and decreased systemic vascular resistance. Absence of the hormone causes congenital hypothyroidism, characterised by poor brain growth, quick stature, and immature skeletal development. In adults, thyroid hormone supports bone transforming and degradation of pores and skin and hair. T3 binds to thyroid hormone receptor subtypes liable for the assorted actions of thyroid hormone. Describe the anatomy and microscopic anatomy of the adrenal gland, together with the chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla and the three zones of the adrenal cortex. Explain the enzymatic reactions involved in producing norepinephrine and epinephrine and integrate those reactions with the regulation of epinephrine synthesis and secretion by the adrenal medulla. Utilize the particular actions of catecholamines to explain an general sympathetic response to a stress imposed on the body. Compare the steroidogenic pathways inside the zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, and zona reticularis with respect to widespread and zona-specific reactions. Describe the mechanism of motion of glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, including the cross-reactivity of cortisol with the mineralocorticoid receptor, and the mechanism to forestall this. Map out the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, including the "loophole" in the suggestions mechanisms that results in excessive androgen production. In addition the adrenal glands regulate salt and volume homeostasis via the steroid hormone aldosterone. Anatomy the adrenal glands are bilateral buildings situated immediately above the kidneys (ad, close to; renal, kidney). In adults the adrenal cortex is composed of three zones-the zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata, and the zona reticularis-that produce mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, and adrenal androgens, respectively. Soon after the cortex types, neural crest�derived cells associated with the sympathetic ganglia, called chromaffin cells, migrate into the cortex and become encapsulated by cortical cells. Thus the chromaffin cells set up the internal portion of the adrenal gland, which known as the adrenal medulla. The chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla have the potential to develop into postganglionic sympathetic neurons. They are innervated by cholinergic preganglionic sympathetic neurons and may synthesize the catecholamine neurotransmitter norepinephrine from tyrosine. I n adults the adrenal glands emerge as fairly complex endocrine structures that produce two structurally distinct lessons of hormones: steroids and catecholamines. The catecholamine hormone epinephrine acts as a fast responder to stresses similar to hypoglycemia and train to regulate multiple parameters of physiology, including vitality metabolism and cardiac output. About 80% of the cells of the adrenal medulla secrete epinephrine, and the remaining 20% secrete norepinephrine. Although circulating epinephrine is derived entirely from the adrenal medulla, solely about 30% of the circulating norepinephrine comes from the medulla. The remaining 70% is released from postganglionic sympathetic nerve terminals and diffuses into the vascular system. Synthesis of Epinephrine the enzymatic steps in epinephrine synthesis are shown in. Within the granule, all dopamine is completely transformed to norepinephrine by the enzyme dopamine -hydroxylase. Epinephrine is then transported again into the granule for storage and to bear regulated exocytosis. The primary autonomic facilities that provoke sympathetic responses reside in the hypothalamus and brainstem, and they receive input from the cerebral cortex, the limbic system, and other regions of the hypothalamus and brainstem. It additionally increases the exercise of dopamine -hydroxylase and stimulates exocytosis of the chromaffin granules.
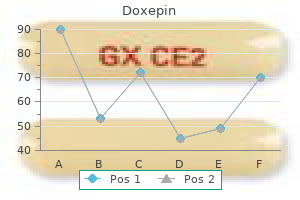
Purchase cheapest doxepin and doxepin
Larger insertions and deletions arise through a quantity of mechanisms, together with retrotransposition (such as for Alu repeat sequences) and illegitimate recombination at sites of sequence homology (a frequent finding in microdeletion syndromes). This high mutation fee makes microsatellites useful as markers for genetic mapping: they mutate incessantly enough to be highly polymorphic in a population but are secure enough to be transmitted reliably in a pedigree. Simple sequence repeats (microsatellites) happen roughly every 30 kilobases in the human genome (depending on the repeat-length threshold used), and a high proportion are polymorphic, to some extent, across human populations. These markers are easily assayed on a moderate scale but still have to be resolved by electrophoresis. Although this is practicable on a modest scale, similar to diagnostic analysis for linkage to a mapped however nonetheless unknown disease mutation segregating within a household, identifying the correct measurement of each allele is essentially the most important bottleneck for purposes requiring very high throughput with many markers. On average, any two copies of the human genome have 1 polymorphism in roughly each one thousand base pairs. Identifying New Disease Genes Linkage knowledge to identify new disease genes are analyzed by laptop algorithms that assess their statistical significance. Although many linkage evaluation packages can be found, a recurrent query arises with respect to the statistical threshold for declaring linkage. As pointed out by Lander and Kruglyak,87 each genome scan is really a sequence of discrete hypotheses. Statistical thresholds have to be set to account for the number of hypotheses examined. Lander and Kruglyak argued that in the current era, the variety of hypotheses that must be accounted for in linkage studies is a function of genome size, as a end result of one continues testing markers until the genome is roofed. They advised using statistical thresholds based on the chance of false-positive findings in a whole genome linkage scan (genome-wide significance) rather than in a discrete take a look at of any one specific locus (point-wise significance). Computer simulations in the absence of linkage and permutation testing of real linkage knowledge help the concept that genome-wide significance levels are needed to decrease reporting of false-positive findings. Association and Linkage Disequilibrium A concept associated to linkage analysis is genetic affiliation. Rather than explicitly following coinheritance of traits and markers by way of a family pedigree, association research comply with covariation of traits and markers in a inhabitants. Case and control samples are in contrast for alleles at every locus to determine whether or not a quantity of alleles are considerably overrepresented (disease-associated alleles) or underrepresented (protective alleles) in illness instances. Linkage disequilibrium primarily means that specific alleles at two loci are inherited together throughout a inhabitants. This happens when the genetic distance between the loci is small compared with the number of generations by which the 2 alleles could have separated by recombination in that population. Association studies that take finest advantage of population-based linkage disequilibrium may present the following opportunity to discover genes that act in multifactorial and genetically heterogeneous diseases. A substantial number of these research first appeared in 2007, including a big study that mixed analysis of several unrelated illnesses and traits concurrently. Conclusion Genetics plays an important position in the day-to-day apply of obstetrics. Clinical genetics will more and more turn out to be a self-discipline that physicians might be expected to use for the care of their patients. Research in molecular biology and molecular genetics, along with the genetic info supplied by the Human Genome Project and genomics, will present the data needed for physicians to formulate new medical approaches to medical diagnostics and therapeutics. Wynshaw-Boris-for the group and many of the figures and tables used within the present chapter. International HapMap Consortium: A haplotype map of the human genome, Nature 437:1299, 2005. Johnson J, Canning J, Kaneko T, et al: Germline stem cells and follicular renewal in the postnatal mammalian ovary, Nature 428:6979, 2004. In Milunsky A, editor: Genetic disorders in the fetus, ed 4, Baltimore, 1998, Johns Hopkins University Press, p 179. Sebat J, Lakshmi B, Malhotra D, et al: Strong association of de novo copy number mutations with autism, Science 316:5823, 2007.
Order generic doxepin online
An overly fast fee of atresia or growth will deplete the reserve and give rise to untimely ovarian insufficiency. Pituitary gonadotropins preserve a normal ovarian reserve by promoting the overall well being of the ovary. However, the speed at which resting primordial follicles enter the expansion course of seems to be independent of pituitary gonadotropins. The choice of a resting follicle to enter the early progress part is primarily depending on intraovarian paracrine elements produced by both the follicle cells and oocytes. The Gamete In primordial follicles the gamete is derived from oogonia which have entered the first meiotic division; such oogonia are referred to as main oocytes. Primary oocytes progress through most of prophase of the primary meiotic division Ovarian reserve ~300,000 primordial follicles at menarche Growth ~30,000 primordial follicles Ovulation ~450 dominant follicles Atresia ~270,000 primordial follicles Atresia About 30,000 major, secondary, or tertiary follicles �. This stage is characterized by the decondensation of chromatin, which helps the transcription needed for oocyte maturation. Meiotic arrest at this stage, which can final for as much as 50 years, seems to be due to "maturational incompetence," or lack of the cell cycle proteins needed to assist the completion of meiosis. The nucleus of the oocyte, called the germinal vesicle, remains intact at this stage. Blood vessels Primary oocyte Early antral follicle Antrum Cumulus cells Blood vessel Germinal vesicle Zona pellucida Basal lamina Mural granulosa cells Theca Growing Preantral Follicles Growth and Structure the first stage of follicular development is preantral, which refers to the development that occurs before the formation of a fluid-filled antral cavity. One of the primary seen signs of follicle growth is the appearance of cuboidal granulosa cells. Once a secondary follicle acquires three to six layers of granulosa cells, it secretes paracrine factors that induce nearby stromal cells to differentiate into epithelioid thecal cells. Once a thecal layer forms, the follicle is referred to as a mature preantral follicle. In people it takes several months for a primary follicle to reach the mature preantral stage. Follicular development is associated with an inward motion of the follicle from the outer cortex to the internal cortex, closer to the vasculature of the ovarian medulla. Follicles release angiogenic factors that induce development of 1 to two arterioles that type a vascular wreath around the follicle. The Gamete Large recruitable antral follicle Primary oocyte Germinal vesicle Zona pellucida Cumulus cells Basal lamina Mural granulosa cells Theca �. The zona pellucida will increase in thickness and supplies a species-specific binding site for sperm throughout fertilization (see Pregnancy). Importantly, granulosa cells and the oocyte maintain gap junctional contact by way of mobile projections by way of the zona pellucida. The oocyte also continues to secrete paracrine components that regulate follicle cell growth and differentiation. Thus the most important product of theca cells is androstenedione versus testosterone. The main distinction Mature preantral follicles become early antral follicles. Once the granulosa epithelium will increase to six to seven layers, fluid-filled areas appear between cells and coalesce into the antrum. Over a interval of about forty five days, this wave of small antral follicles will continue to develop to massive recruitable antral follicles which may be 2 to 5 mm in diameter. This interval of progress is characterized by a few 100-fold enhance in granulosa cells (from about 10,000 to 1,000,000 cells). It is also characterised by swelling of the antral cavity, which more and more divides the granulosa cells into two discrete populations: mural granulosa cells and cumulus cells. Mural granulosa cells (also known as the stratum granulosum) form the outer wall of the follicle. Primary oocyte arrested at prophase I As oocyte grows, it synthesizes sufficient proteins. Mural granulosa cells turn into extremely steroidogenic and stay in the ovary after ovulation to differentiate into the corpus luteum. Cumulus cells are the inner cells that surround the oocyte (they are additionally referred to as the cumulus oophorus and corona radiata). The innermost layer of cumulus cells maintains gap and adhesion junctions with the oocyte.
Cheap doxepin 75 mg with amex
Airway resistance normally accounts for about 20% of the work of breathing. Pathophysiology observe: Airway diameter could be decreased (and airway resistance thereby increased) by a number of mechanisms. Pharmacology note: Many lessons of medicine affect large-airway diameter by affecting bronchial clean muscle tone. For instance, b2-adrenergic agonists such as albuterol instantly stimulate bronchodilation. Pathology observe: In emphysema, compliance work is lowered due to the destruction of lung tissue and the loss of elastin and collagen. In pulmonary fibrosis, compliance work is elevated, as a end result of the fibrotic tissue requires more work to expand. Tissue resistance: usually small element of labor of respiratory because of presence of pleural fluid 4. Tissue resistance � As the pleural surfaces slide over each other through the respiratory cycle, friction and due to this fact resistance is generated. Respiratory Physiology Pathology observe: In sure pleuritic situations, inflammation or adhesions are fashioned between the 2 pleural surfaces, which will increase tissue resistance considerably. As elastance increases, more and more higher strain modifications will be required to distend the lungs. Clinical notice: In restrictive lung ailments corresponding to silicosis and asbestosis, inspiration turns into increasingly difficult as the resistance to lung expansion increases in response to elevated lung elastance, resulting in lowered lung volumes and total lung capacity. Expiration may due to this fact turn out to be an active process (rather than a passive one), even while at relaxation, as a outcome of the simply collapsible airways "trap" air within the lungs. The water molecules are interested in each other through noncovalent hydrogen bonds and are repelled by the hydrophobic alveolar air. The engaging forces between water molecules generate surface pressure (T), which in turn produces a collapsing stress, which acts to collapse the alveoli. Alveolus Attractive force Alveolar fluid (without surfactant) Repulsion due to lipid Alveolar fluid (with surfactant) Surfactant and the hydrophobic "tail" in the alveolar air. Polar head Lipid tail 5-9: Role of surfactant in lowering alveolar surface rigidity. Atelectatic lung might outcome from external compression, as might happen with pleural effusion or tumor; a prolonged period of "shallow breaths," as might occur with ache. Mothers in premature labor are incessantly given corticosteroids to stimulate the fetus to produce surfactant. Palv, Alveolar partial pressure; Part, arterial partial pressure; Pven, venous partial stress. In the upright place, when the effects of gravity are apparent, the lung apices are comparatively underperfused, whereas the lung bases are comparatively overperfused. Lung apices: relatively underperfused in upright position owing to low arterial hydrostatic stress at lung apices Zone 1 has no blood flow through the cardiac cycle. Zone 1 blood move: could additionally be seen with severe hemorrhage and positivepressure ventilation 152 Rapid Review Physiology 3. Zone 2 blood move � Zone 2 has intermittent blood move in the course of the cardiac cycle, with no blood flow during diastole. This sample of blood circulate is attribute of the lung bases, that are located below the guts. The catheter is inserted through a central vein and advanced into the pulmonary artery. An inflated balloon at the distal tip of the catheter allows it to "wedge" into a distal department of the pulmonary artery. Zone three blood move: primarily happens within the lung bases V/Q matching: important for efficient gas trade V/Q matching: inefficient to perfuse unventilated alveoli or ventilate nonperfused alveoli Lung apices comparatively overventilated at rest Lung bases comparatively overperfused at relaxation Mechanisms of V/Q matching: hypoxiainduced vasoconstriction, pulmonary hemodynamic and ventilatory changes with exercise C. Mechanisms of sustaining V/Q matching � Optimal matching of pulmonary air flow and perfusion is achieved by hypoxiainduced vasoconstriction and by changes in response to exercise. However, in the pulmonary vasculature, hypoxia stimulates vasoconstriction of pulmonary arterioles, essentially preventing the perfusion of poorly ventilated lung segments. During train, further capillaries open (recruitment) because of increased pulmonary artery blood strain. Anatomic shunt � this happens when blood that might normally go to the lungs is diverted elsewhere. In the fetus, gasoline change occurs in the placenta, so many of the cardiac output both is shunted from the pulmonary artery to the aorta via the ductus arteriosus or passes by way of the foramen ovale between the proper and left atria.
25 mg doxepin sale
This sellar diaphragm is pierced by the pituitary stalk and the hypophyseal vessels. Chronic pulsatile pressure exerted by the cerebrospinal fluid may broaden the sella, leading to the appearance of an enlarged, "empty sella," which can be associated with hypopituitarism in some sufferers. The anatomic relationship between the pituitary gland and the optic chiasm is clinically necessary, because mass lesions inside the pituitary could compress either the chiasm or different parts of the optic apparatus, giving rise to quite so much of visible field defects. Specific locations where the arachnoid separates from the pia mater form cisterns full of cerebrospinal fluid, together with the chiasmatic cistern and the interpeduncular cistern. These areas could be distorted by space-occupying sellar lesions growing superiorly from the pituitary. The hypothalamus is positioned superiorly to the pituitary gland and is bounded between the optic chiasm anteriorly, the caudal border of the mammillary our bodies posteriorly, and the hypothalamic sulcus superiorly. Distinct hypothalamic nuclei regulate anterior pituitary perform through the synthesis of several stimulating hormones (growth hormone�releasing hormone, corticotropin-releasing hormone, thyrotropin-releasing hormone, and gonadotropin-releasing hormone) and inhibiting hormones (somatostatin and dopamine), launched at neuronal axon terminals present within the median eminence and the infundibulum. These hormones are carried through the hypophyseal portal system to the adenohypophysis, where they regulate hormone secretion in a particular manner. The inter-relationships between the hypothalamus and the posterior pituitary are detailed in Plate 5-26. Large lesions arising above the sella could impinge on the hypothalamus, interfering with its functions. The cavernous sinuses are located laterally to the pituitary gland, and receive blood from the pituitary by way of the hypophyseal veins. Each cavernous sinus contains a quantity of essential structures, together with the cavernous portion of the ipsilateral internal carotid artery, the oculomotor, trochlear, and abducens nerves, in addition to the primary two divisions (ophthalmic and maxillary) of the trigeminal nerve. Each of these nerves could also be impinged upon by space-occupying lesions arising in the sella that extend Fornix Interventricular foramen Hypothalamic sulcus Anterior commissure Lamina terminalis Tuber cinereum Mammillary physique Chiasmatic cistern Optic chiasm Diaphragma sellae Interpeduncular cistern Pituitary gland Sphenoidal sinus Nasal septum Nasopharynx Pontine cistern Corpus callosum Choroid plexus of 3rd ventricle Thalamus Pineal gland into the cavernous sinus. Examples of such lesions include meningiomas, chondrosarcomas and sellar metastases. Characteristically, pituitary adenomas solely rarely trigger dysfunction of cranial nerves inside the cavernous sinuses, with the notable exception of adenomas present process hemorrhagic necrosis (pituitary apoplexy). The circular sinus lies between the pituitary gland and the underlying sphenoid bone in the sella, forming interconnections between the two cavernous sinuses. The thin sellar floor separates the pituitary gland from the underlying sphenoid sinus. The sellar ground can be expanded by slowly growing sellar lots, leading to reworking of the sella, or eroded by sellar plenty rising inferiorly. The shut relationship between the sella, the sphenoid sinus, and the nasopharynx offers an essential entry path to pituitary surgeons. Using a trans-sphenoidal method, many sellar masses can be resected with low morbidity. At the optic chiasm, axons of the retinal ganglion cells that originate in the nasal portion of each retina cross to the contralateral facet. In contrast, nerve fibers from the temporal portion of each retina remain on the ipsilateral side previous the chiasm to kind every optic tract, accompanied by nerve fibers crossing from the nasal portion of the contralateral retina. In addition to benign pituitary adenomas, which account for roughly 90% of mass lesions in surgical series, there are a large quantity of pathologic sellar mass lesions. Mass lesions extending superiorly from the sella often impinge on the optic chiasm, which is generally located directly above the diaphragma sellae (in approximately 90% of individuals). Early abnormalities that happen on account of chiasmatic compression embrace loss of color perception because of optic neuropathy, which may be documented using commonplace Ishihara chart testing, as well as variable loss of peripheral (temporal) subject imaginative and prescient. Among patients with mass lesions growing from the sella, vision is mostly misplaced first in both or each superior temporal quadrants. In contrast, mass lesions arising at the base of the hypothalamus, which compress the optic chiasm from above, might lead to early lack of vision in the inferior temporal quadrants. Compression of the prechiasmatic optic nerves may lead to ipsilateral optic neuropathy, giving rise to a central scotoma. Lesions that compress the anterior portion of the chiasm on one side might give rise to ipsilateral optic neuropathy (central scotoma) and loss of peripheral imaginative and prescient within the contralateral superior temporal quadrant, a constellation termed "junctional scotoma. Primary optic atrophy is current in circumstances of long-standing nerve fiber compression.
Real Experiences: Customer Reviews on Doxepin
Cobryn, 23 years: This space receives quite a few connections from the temporal and parietal lobes by way of pathways in the cingulum, a bundle of lengthy affiliation fibers lying within the cingulate gyrus. Radiotherapy has been related to significantly higher survival in choroid plexus carcinomas.
Altus, 63 years: In adipocytes it mobilizes fatty acids and glycerol from triacylglycerol by mixed direct and oblique activation of adipocyte lipases. Ip S, Chung M, Raman G, et al: Breastfeeding and maternal and toddler well being outcomes in developed countries, Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep) 153:1�186, 2007.
Kaelin, 41 years: Estrogens enhance breast growth directly and indirectly through stimulation of maternal pituitary prolactin manufacturing. With the widespread use of the oral polio virus vaccine, which incorporates stay, attenuated poliovirus strains, vaccineassociated paralytic poliomyelitis was first acknowledged.
Murak, 45 years: Explain modifications within the female tract, with emphasis on the uterine endometrium, in the course of the menstrual cycle. The other (gray), by binding each to postsynaptic receptors and presynaptic autoreceptors, can affect both postsynaptic goal and activities of the presynaptic terminal.
Vasco, 53 years: When tumors within the region of the pituitary gland injury this part of the hypothalamus, feeding circuits turn into disinhibited and the affected person becomes obese. It additionally decreases the secretion of thick mucus and relaxes the tone within the isthmus.
Jerek, 34 years: Often, the very important signs are unstable, with an irregular pulse and a risky blood strain. Meningiomas arising at the cerebellopontine angle can produce sensorineural listening to loss.
Fabio, 57 years: Mannitol given intravenously increases the osmotic gradient between blood and tissues. If a gamete is chromosomally unbalanced, the odds are increased for spontaneous abortion.
Rune, 51 years: In this stage, the more basic phenotype is observed, with lowered facial mobility, stooped posture when standing, lowered arm swing on walking, and en bloc turning, Rapid alternating movements are impaired. The Cervix Structure and Function the cervix is the inferior extension of the uterus that initiatives into the vagina.
10 of 10 - Review by J. Thordir
Votes: 166 votes
Total customer reviews: 166
References
- Noel G, Giocanti N, Fernet M, et al. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP-1) is not involved in DNA doublestrand break recovery. BMC Cell Biol 2003;4:7.
- Babbitt DP, Dobbs J, Boedecker RA: Multiple bladder diverticula in Williams eElfin-Faciesi syndrome, Pediatr Radiol 8:29n31, 1979.
- Bedard EL, Inculet RI, Malthaner RA, et al: The role of surgery and postoperative chemoradiation therapy in patients with lymph node positive esophageal carcinoma. Cancer 91:2423, 2001.
- Scholz M, Cinatl J, Schadel-Hopfner M, Windolf J. Neutrophils and the blood-brain barrier dysfunction after trauma. Med Res Rev. 2007;27:401-416.
- Cowley Jr AW, Roman RJ. Control of blood and extracellular volume. Baillieres Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1989;3(2):331-69.
- Lewis MI, Fournier M, Storer TW, et al. Skeletal muscle adaptations to testosterone and resistance training in men with COPD. J Appl Physiol 2007; 103: 1299-1310.
- Khan IA. Clinical and therapeutic aspects of congenital and acquired long QT syndrome. Am J Med 2002;112:58-66.
- Lorente L, et al. Association between serum soluble CD40 ligand levels and mortality in patients with severe sepsis. Crit Care. 2011;15:R97.

