Molenzavir dosages: 200 mg
Molenzavir packs: 40 caps, 80 caps, 120 caps, 160 caps, 200 caps

Buy molenzavir master card
Because the sensor continually feeds information back to the control middle, the furnace might be routinely shut off when the temperature has returned to regular. Tubes, such because the digestive tract and respiratory tract, bring the exterior setting to deeper parts of the bag the place substances could be absorbed into the inner fluid environment or excreted into the external surroundings. All the "accessories" by some means assist maintain a constant environment inside the bag that permits the cells that live there to survive. Although not common, optimistic feedback loops do exist within the physique and are typically additionally involved in regular function. This sort of suggestions loop causes an ever-increasing fee of events to occur till something stops the process. Another instance is the more and more rapid sticking collectively of blood cells known as platelets to type a plug that begins formation of a blood clot. In every of these cases, the process will increase rapidly until the optimistic suggestions loop is stopped all of a sudden by the delivery of a child or the formation of a clot. In the long run, such normal optimistic suggestions occasions also assist preserve constancy of the internal environment. However, adverse suggestions can abnormally flip into constructive suggestions, probably inflicting a lethal shift in physique perform. For instance, severe bleeding may cause a drop in blood stress (needed for continued blood flow), so the guts beats sooner to improve the blood strain again to regular, whereas also rising the lack of blood, which causes a further drop in blood stress and a good quicker heart rate in an ever-increasing cycle. The amplification of blood loss caused by this constructive feedback loop can rapidly turn lethal. To cease the constructive feedback loop, one could apply stress to the wound to stop or gradual the loss of blood. It is important to notice that ordinary homeostatic control mechanisms can preserve only a relative constancy. Because all organs operate to help preserve homeostatic steadiness, we discuss unfavorable and optimistic feedback mechanisms often all through the remaining chapters of this book. Nerve endings that act as temperature sensors feed information to a control heart in the mind that compares precise physique temperature to normal physique temperature. We cease shivering when feedback information tells the brain that physique temperature has increased to regular. Most homeostatic management loops in the physique involve adverse feedback as a result of reversing changes again toward a normal worth tends to stabilize conditions - precisely what homeostasis is all about. An instance of a adverse suggestions loop happens when growing blood carbon dioxide focus brought on by muscles producing further carbon dioxide during train is counteracted by an increase in breathing to convey the blood carbon dioxide level back down to regular. A thermostat (control center) receives suggestions info from a thermometer (sensor) and responds by counteracting change from regular by activating a furnace (effector). The mind (control center) receives feedback information from nerve endings referred to as chilly receptors (sensors) and responds by counteracting a change from regular by activating shivering by muscles (effectors). For example, many have an interest within the advanced control mechanisms that preserve or restore homeostasis during or immediately after durations of strenuous physical exercise. Exercise, defined as any important use of skeletal muscles, is a normal activity with useful outcomes. These and lots of different physique capabilities rapidly deviate from "normal ranges" that exist at relaxation. As a scientific self-discipline, train physiology usually attempts to explain many physique processes in terms of how they preserve homeostasis. Exercise physiology has many practical purposes in therapy and rehabilitation, athletics, occupational health, and basic wellness. This specialty issues itself with the function of the entire body, not just one or two physique methods. As the baby is pushed from the womb (uterus) into the delivery canal (vagina), stretch receptors detect the movement of the child. Uterine contractions rapidly get stronger and stronger till the baby is pushed out of the body and the constructive suggestions loop is damaged. During childhood, homeostatic functions progressively become more and more efficient and effective. During late adulthood and old age, they gradually turn into much less and less environment friendly and efficient.
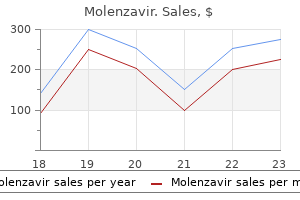
Cheap 200 mg molenzavir amex
Nerve provide By ventral rami of the decrease three cervical (C6, C7, and C8) spinal nerves. When the 2nd rib is fastened, it bends the cervical vertebral column to the identical facet. When upper attachment is fixed, it helps to elevate the 2nd rib and thus acts as an accessory muscle of respiration. When upper finish is fastened, it elevates the primary rib and thus acts as an adjunct muscle of respiration. It is the important thing muscle on the root of neck because of its intimate relations to many constructions on this region. Origin From anterior tubercles of transverse processes of C3, C4, C5, and C6 vertebrae. Origin From posterior tubercles of the transverse processes of C2 C6 cervical vertebrae. Insertion On to the higher floor of the primary rib between the tubercle of the rib and groove for subclavian artery. Pre- and Paravertebral Regions and Root of the Neck 171 Insertion the fibres converge and descend nearly vertically to be inserted by a slim, flat tendon to the scalene tubercle on the internal border of the 1st rib and to the ridge on the upper floor of the rib anterior to the groove for the subclavian artery. Acting from below, it bends the neck forwards and laterally and rotates it to the other facet. Acting from above, it helps to elevate the first rib and thus acts as an accessory muscle of respiration. Phrenic nerve runs downward across the anterior surface of the muscle deep to prevertebral fascia. Two arteries - transverse cervical and suprascapular - cross the anterior surface of muscle from medial to lateral facet. Two muscle tissue (a) Inferior stomach of omohyoid crosses the anterior surface from medial to lateral side. Subclavian artery passes deep to scalenus anterior close to its insertion from medial to lateral side, separating it from scalenus medius. The medial border of scalenus anterior varieties the lateral boundary of the scalenovertebral triangle or triangle of the vertebral artery. The lateral border of the scalenus anterior is related to trunks of brachial plexus, which emerge underneath it. The upper part of scalenus anterior is separated from longus capitis by the ascending cervical artery. Clinically, this syndrome presents as: (a) tingling sensation and numbness along the inner border of forearm and hand, i. Roof: Contents: (a) transverse means of C7 vertebra, (b) ventral ramus of C8 spinal nerve, which passes laterally above the neck of first rib, (c) neck of first rib, and (d) cupola of cervical pleura. Boundaries: Medial: Lateral: Apex: Base: Floor (posterior wall): Lower indirect part of the longus colli. The artery extends upwards vertically from the base to enter the foramen transversarium of C6 on the apex. Thyrocervical trunk and inferior thyroid artery; the later arches medially across the apical a half of the triangle. Thoracic duct on the left aspect arches laterally on the level of transverse strategy of C7 vertebra. Scalenus minimus (pleuralis): the scalenus minimus is the fourth rudimentary scalene muscle. It arises from the anterior border of the transverse process of C7 vertebra and inserted to the internal border of the first rib behind the groove for the subclavian artery and to the dome of the cervical pleura. Pre- and Paravertebral Regions and Root of the Neck 173 rami of C2C4 divide into higher and lower branches. The ventral ramus of C1 and branches of C2C4 ventral rami are related with each other to kind three loops, therefore cervical plexus can be called plexus of loops.
Syndromes
- Ointments containing hormones
- Little to no urine output
- Thyroid peroxidase (TPO) antibody
- Diagnose cancer
- Fluid buildup of the legs (edema) and in the abdomen (ascites)
- Stomach pain (with possible bleeding in the stomach and intestines)
- Possible drainage, if there is an infection
- What other symptoms do you have?
- Valve replacement or repair
Discount 200mg molenzavir with mastercard
Branches From the Main Trunk Two branches arise from the main trunk, a sensory branch (nervus spinosus) and a motor branch (nerve to medial pterygoid): 1. Nervus spinosus (meningeal branch): It takes a recurrent course to enter the cranial cavity by way of foramen spinosum with center meningeal artery and provides the dura mater of the center cranial fossa. Nerve to medial pterygoid: It arises from the medial aspect of the principle trunk, near the otic ganglion traverses via the ganglion and provides the medial pterygoid from its deep aspect. In addition to medial pterygoid it also provides tensor palati and tensor tympani muscular tissues. From the Anterior Division the anterior division is especially motor and offers branches to all muscular tissues of mastication besides medial pterygoid, which is equipped by nerve to medial pterygoid from the principle trunk. Masseteric nerve: It emerges on the upper border of the lateral pterygoid, just in entrance of the temporomandibular joint, passes laterally by way of the mandibular notch, along with masseteric artery to supply the masseter from its deeper side. The anterior and posterior temporal nerves emerge at the higher border of the lateral pterygoid and ascend up in the temporal fossa to provide the temporalis muscle from its deep facet. Nerve to lateral pterygoid: It runs with the buccal nerve and enters the deep surfaces of each the heads of lateral pterygoid muscle, which it provides. It emerges between the two heads of the lateral pterygoid and programs downwards and forwards onto the buccinator muscle, giving branches to the skin of the cheek. It then pierces the buccinator muscle and provides the mucus membrane of the cheek and gum of the lower jaw opposite the molars and second premolar teeth. All the branches of anterior division of the mandibular nerve are motor besides buccal nerve which is sensory. Auriculotemporal nerve: this nerve arises by two roots, which after encircling the middle meningeal artery unite to form the single trunk. It runs backwards between the neck of the mandible and the sphenomandibular ligament. Behind the neck of the mandible, it turns upwards and ascends over the root of zygoma to enter the temple behind the superficial temporal vessels. Distribution: (a) Its auricular branches supply skin of the tragus, higher a part of the pinna, exterior auditory meatus and tympanic membrane. The lower elements of these regions are provided by nice auricular nerve and auricular branch of the vagus nerve. Lingual nerve: It is the smaller terminal branch of posterior division of the mandibular nerve. It is sensory to the mucus membrane of anterior two-third of the tongue besides vallate papillae. It runs first between tensor palati and lateral pterygoid and then between lateral and medial pterygoids. After emerging on the lower border of the lateral pterygoid, it first run downwards and forwards between the ramus of the mandible and medial pterygoid, comes in direct contact with the mandible where the bone is thinned to type a shallow groove below and medial to the last molar tooth, just above the posterior end of the mylohyoid line. This groove separates the attachments of pterygomandibular raphe above and mylohyoid muscle beneath. It enters the mouth on the superior floor of the mylohyoid, after which it crosses the styloglossus to attain the lateral floor of the hyoglossus. Here it winds round the submandibular duct (first above, then lateral, then under and eventually medial to the duct) and divides into its terminal branches. Distribution: (a) Provides sensory provide to ground of mouth, lingual surface of the gum and anterior two-third of the tongue; (b) Carries preganglionic secretomotor fibres to submandibular and sublingual salivary glands. Inferior alveolar nerve: It is the larger terminal department of the posterior division of mandibular nerve. Course: It emerges beneath the lower head of the lateral pterygoid and passes vertically downwards and ahead on the medial pterygoid. The nerve lies anterior to inferior alveolar vessels between the sphenomandibular ligament and the ramus of the mandible. Then enters the mandibular foramen in firm with inferior alveolar artery, traverses the mandibular canal so far as mental foramen, the place it terminates by dividing into psychological and incisive branches. Branches: (a) Nerve to mylohyoid arises from the inferior alveolar nerve before it enters the mandibular canal. While performing inferior alveolar nerve block, if needle is inserted too far posteriorly, it might enter the parotid gland and harm the facial nerve resulting in transient facial palsy. The nerve can be at risk throughout surgical removing of the submandibular salivary gland, throughout which the submandibular duct have to be dissected out fastidiously from the nerve. Thus in sufferers affected by tongue most cancers, the ache radiates to the ear and to the temporal fossa in the space of distribution of auriculo-temporal nerve.
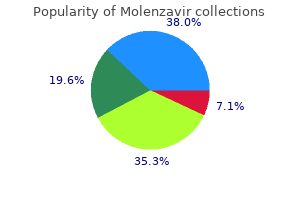
Discount 200 mg molenzavir otc
These buildings are bounded anteriorly by pretracheal fascia, which extends on both side to merge with the investing layer of deep cervical fascia deep to sternocleidomastoid. On both facet of the midline tubes are several ascending and descending neurovascular structures, corresponding to carotid tree consisting of frequent carotid, inside carotid and external carotid arteries, inside jugular vein and last 4 cranial nerves. At the higher end these buildings enter or go away the skull by way of varied foramina within the base of the skull, viz. This musculoskeletal block is bounded by prevertebral fascia, which merges behind on both side with the deep fascia enclosing the trapezius muscle. The vertebral canal inside the cervical vertebral column provides passage to the spinal twine. The roots of cervical spinal nerves come out through intervertebral foramina in this region. The ventral rami of the first 4 cervical nerves kind the cervical plexus and ventral rami of the decrease 4 cervical nerves along with ventral ramus of T1 type the brachial plexus. The spinal wire, digestive and respiratory tracts, and main blood vessels traverse this highly flexible area. The neural structures present in the region include: final four cranial nerves and cervical and brachial plexuses. A newborn baby has no visible neck because his or her decrease jaw and chin touches the shoulders and thorax. The following structures may be simply palpated in the anterior region of the neck. Hyoid bone: It is located in a despair behind and slightly below the chin and can be easily felt if the neck is slightly extended. The hyoid bone could be gripped between the thumb and index finger and moved from facet to side. The thyroid notch, the curved higher border of the thyroid cartilage could be simply palpated. Tracheal rings: these can be palpated beneath the cricoid cartilage by urgent gently backwards above the jugular notch. Isthmus of the thyroid gland: It lies on the front of the 2nd, third, and 4th tracheal rings and may be palpated. Suprasternal (jugular) notch: It is a depression simply superior to sternum between the medial expanded ends of the clavicle and can be simply palpated. Transverse process of atlas vertebra Mastoid process Angle of mandible Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Hyoid bone Thyroid cartilage Cricoid cartilage Isthmus of thyroid gland Tracheal rings the vertebral ranges of a few of the structures that may be palpated within the anterior midline of the neck are given in Table 1. Thyroid lobe: It could be palpated on either aspect slightly below the extent of cricoid cartilage. Common carotid artery: It may be observed and palpated on both side on the level of junction between the larynx and trachea along the anterior border of sternocleido-mastoid muscle. When the pinnacle is turned to the opposite side it varieties a distinguished raised ridge that extends diagonally from mastoid process to sternum. The tendon of this muscle becomes especially distinguished to the side of the jugular notch. Trapezius: the anterior border of trapezius becomes outstanding when the individual is asked to shrug his shoulder against the resistance. External jugular vein: It may be seen because it crosses obliquely across the sternocleidomastoid muscle, notably if a person is offended or if the collar of his shirt is merely too tight. Transverse process of the atlas vertebra: It may be felt on deep strain halfway between the angle of the mandible and the mastoid process. Clinical correlation Cervical lymph nodes in the lateral area of the neck typically become swollen and painful from infections of the oral and pharyngeal regions. Ligamentum nuchae: It is raised when the neck is flexed and extends from backbone of C7 vertebra below to the exterior occipital protuberance above. Clinical correlation Clinically, the posterior region of neck is extremely essential because of the debilitating harm it sustains from whiplash damage or a damaged neck. External occipital protuberance: It can be simply palpated with inion at its summit at the higher end of nuchal furrow within the posterior midline of the neck.
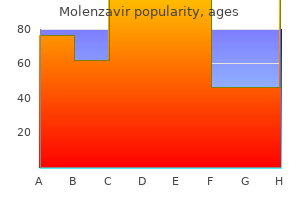
Purchase 200mg molenzavir
Thereafter, it joins the ventral ramus of C2 to participate within the formation of cervical plexus. They are characterised by the presence of foramen in each of their transverse processes referred to as foramen transversarium. It is named after mythological Greek Titan who was reputed to help the heavens on his shoulders. The 2nd cervical vertebra is called axis, because its odontoid course of types a pivot around which atlas rotates and carries the cranium. The axis possesses, tooth-like odontoid process which projects upwards from the physique. Synovial (joints of Luschka), between the lateral margins of the bodies of adjacent vertebrae. The adjacent articular surfaces are lined by the plates of hyaline cartilage and held collectively by an intervertebral disc. It consists of an outer half fashioned by a collection of fibrocartilaginous laminae known as annulus fibrosus and an inner half consisting of jelly-like materials known as nucleus pulposus. The most peripheral laminae of annulus fibrosus are formed of pure collagenous tissue and on the front and on the back they mix with sturdy anterior and the weak posterior longitudinal ligaments. The discs are firmly bound to the sides of the hyaline cartilages and our bodies of the vertebrae. The intervertebral discs are thick anteriorly within the cervical region contributing to the anterior convexity of the neck. The intervertebral disc together with hyaline cartilage covering the upper and decrease articular surfaces of the adjoining vertebral our bodies type the intervertebral symphysis. The long fibres are superficial and bridge across a quantity of vertebrae whereas quick fibres are deep and bridge across a single pair of vertebrae, and mix with the annulus fibrous of the intervertebral disc. The joints between 1st and 2nd cervical vertebrae and people between 1st cervical vertebrae and cranium permit rotation and nodding of head, respectively. The joints of neck are clinically important as a result of excessive incidence of spondylosis, disc prolapse, and fracture dislocation within the cervical region. They embody joints between the vertebral our bodies, vertebral arches, and vertebral articular processes. Secondary cartilaginous (intervertebral disc) between the bodies of adjacent vertebrae. Back of the Neck and Cervical Spinal Column a hundred and five Clinical correlation Prolapse of intervertebral disc within the cervical area: It normally includes the disc between C5 and C6 or C6 and C7. The nucleus pulposus typically herniates in the posterolateral path and compresses a nerve root. Anterior longitudinal ligament Intervertebral disc Vertebral physique Joints of Luschka (also referred to as uncovertebral joints) the lateral margins of vertebral bodies overlap the edges of intervertebral disc and immediately articulate to kind small synovial joints of aircraft selection called joints of Luschka. Clinical correlation Cervical spondylosis: It is the most typical clinical situation affecting the neck. Degenerative modifications appear within the cervical backbone, often through the third or fourth decade. The disc area between the fifth and sixth cervical vertebrae is most incessantly affected. The earliest changes are confined to the intervertebral disc but the facet joints and uncovertebral joints (joints of Luschka) get entangled soon. The foramina transversaria containing vertebral artery lie lateral to these joints, therefore osteophytes can also cause distortion of vertebral artery leading to vertebrobasilar insufficiency which clinically presents as dizziness and allied signs following jerky neck actions. It is loosely attached to the our bodies to provide space for basivertebral veins and paravertebral venous plexus. Its superficial long fibres bridge throughout three or 4 vertebrae whereas its short deep fibres prolong between adjacent vertebrae as perivertebral ligaments and are attached to annulus fibrous of the disc. Joints Between the Vertebral Arches Joints between the vertebral arches embrace: 1. The articular surfaces are inclined horizontally and slope inferiorly from anterior to posterior. Between the adjacent spines: Interspinous ligament connects the adjacent spines and supraspinous ligaments connect the information of spinous processes.
Cheap 200mg molenzavir
Plica semilunaris, a small curved fold of conjunctiva instantly lateral to lacrimal caruncle. The potential space between eyelids and eyeball when eyes are closed is called conjunctival sac. The traces of reflexion between palpebral and bulbar conjunctiva above and below form the superior and inferior fornices, respectively. The palpebral conjunctiva is very vascular and firmly adherent to the tarsal plates. On the opposite hand, bulbar conjunctiva is free over the sclera however firmly adherent to the cornea forming its anterior epithelium (the corneal epithelium). When the eyelids are closed, the orbital septum Openings of ciliary glands (along the anterior edge of lid margin) Pupil Lacrimal papilla Lacrimal punctum Lacrimal caruncle Lacus lacrimalis Plica semilunaris Sclera Cilia (eyelashes) Conjunctival Fluid the conjunctival sac is crammed with three films of fluid from within outwards these are: 1. The blinking movements of eyelids make these movies moisten cornea and assist drain the conjunctival fluid into nasal cavity. Clinical correlation · the irritation of conjunctiva (conjunctivitis) as a end result of infection or allergy is doubtless considered one of the commonest ailments of the eye. Palpebral conjunctiva of upper eyelid and ocular conjunctiva - by ophthalmic nerve. Arterial Supply the conjunctiva is supplied by palpebral and anterior ciliary arteries derived from ophthalmic artery. Venous Drainage the venous blood from palpebral conjunctiva is drained into facial vein while from ocular conjunctiva into ophthalmic veins. Lymph Drainage the lymph from conjunctiva is drained into preauricular lymph nodes. The two parts are continuous with one another across the lateral margin of the levator palpebrae superioris. The orbital part is almond formed and situated within the lacrimal fossa within the anterolateral a part of the roof of the bony orbit. The palpebral half is one-third of the size of the orbital half and is located in the lateral part of the upper eyelid below the levator palpebrae superioris and extends as much as the superior fornix of conjunctiva. Ducts of the lacrimal gland: the ducts of lacrimal gland are roughly 12 in number, about 4 or 5 from orbital part and 68 from palpebrae part. Lacrimal gland secretes the lacrimal (tear) fluid and its ducts convey it to conjunctival sac. Ducts from orbital part traverse the palpebral half to open into conjunctival sac. Therefore, elimination of palpebral part of gland is functionally equivalent to elimination of the whole lacrimal gland. Conjunctival sac Nasolacrimal duct Lacrimal fold (valve of Hasner) Inferior meatus of nose Accessory lacrimal glands (glands of Krause): these are very small serous glands located beneath the palpebral conjunctiva near the fornices. Scalp, Temple, and Face sixty five Arterial supply: It is by lacrimal department of ophthalmic artery. Parasympathetic (secretomotor) provide of the lacrimal gland: the pathway of parasympathetic innervation is as follows: (a) the preganglionic parasympathetic fibres come up from lacrimatory nucleus within the pons and cross successively through nervus intermedius, geniculate ganglion, larger petrosal nerve, nerve of pterygoid canal to attain the pterygopalatine ganglion the place they relay. Sympathetic (vasomotor) provide: the pathway of sympathetic innervation is as depicted in Flowchart three. Sensory supply: It is by sensory fibres of lacrimal nerve, a branch of ophthalmic division of trigeminal nerve. Conjunctival sac: It is a potential area between palpebral and bulbar conjunctiva. T1 spinal phase Superior cervical sympathetic ganglion (gives origin to postganglionic sympathetic fibres) Sympathetic plexus round inside carotid artery Deep petrosal nerve Pterygopalatine ganglion Zygomatic nerve Zygomaticotemporal nerve Lacrimal nerve to lacrimal gland Flowchart three. Lacrimal canaliculi: There are two lacrimal canaliculi, superior and inferior in upper and decrease eyelids, respectively. The superior canaliculus at first runs upwards after which bends downwards and medially alongside the free margin of the eyelid to open into the lacrimal sac. The inferior canaliculus at first runs downwards after which bends upwards and medially to open into the lacrimal sac. Lacrimatory nucleus Nervus intermedius Geniculate ganglion Greater petrosal nerve Pterygopalatine ganglion (gives origin to postganglionic parasympathetic fibres) Zygomatic nerve Zygomaticotemporal nerve Lacrimal nerve to lacrimal gland Flowchart 3. It is situated within the deep lacrimal groove bound by posterior lacrimal crest of lacrimal bone and anterior lacrimal crest of frontal means of the maxilla. The sac is 66 Textbook of Anatomy: Head, Neck, and Brain Posterior lacrimal crest Lacrimal part of orbicularis oculi Lacrimal bone Lacrimal sac Lacrimal fascia Minute venous plexus Medial palpebral ligament Lacrimal groove Frontolacrimal suture Minute arterial plexus Frontal strategy of maxilla Anterior lacrimal crest blowing the duct into the eye when one blasts his nostril to clear nasal secretions.
Spanish Jasmine (Jasmine). Molenzavir.
- Liver problems such as hepatitis and cirrhosis, stomach pain due to severe diarrhea (dysentery), increasing sexual desire (aphrodisiac), cancer treatment, use as a sedative, and other uses.
- Dosing considerations for Jasmine.
- How does Jasmine work?
- What is Jasmine?
- Are there safety concerns?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96611
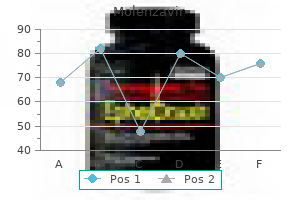
Cheap 200mg molenzavir free shipping
Such models had been exploited for optimization of drugtarget interactions to enhance efficiency and selectivity of lead structures. The availability of X-ray constructions of the protein drug target and dedication of crystal constructions of protein ligand complexes offered extra detailed proteinligand interactions. This structural data has accelerated the drug design and development process [3,4]. With the expansion and developments in structural biology, the three-dimensional structural information of disease-relevant targets additionally expanded quickly. As shown in Chapter 1 X-ray crystal structure-based design contributed to the approval of 34 new drugs by way of 2012. Structure-based design of numerous these marketed drugs and superior scientific candidates will be coated within the next part. The protein could be extracted and purified from a biological matrix, or it may be produced via recombinant strategies or heterologous expression systems. The first technique is extremely time consuming and may be applied solely to proteins which are expressed at a excessive degree. Overexpression of the protein through recombinant strategies is now the tactic of selection, not just for uncommon proteins but also for several applications since it presents a number of advantages. Recombinant proteins are sometimes expressed in micro organism, particularly in Escherichia coli. Bacteria can be dealt with fairly easily, thus furnishing affordable tradition conditions. Furthermore, recombinant methods permit the modification of the protein to enhance its solubility, for the reason that formation of aggregates or inclusion bodies lowers the overall yield of the protein. Several methodologies exist for the modification of the target protein in order to assist expression yield, purification, and crystallizability. Several tags have been developed to be able to enable protein purification by way of affinity chromatography, most commonly used is hexa-His tags for Ni affinity chromatography. The latter two tags are powerful methods of increasing solubility and are most frequently used for that reason. Crystallizability is typically poor because of the presence of highly flexible areas. Protein engineering is rather more handy than restricted proteolysis, which may lead to pattern heterogeneity [6]. Moreover, the solubility of a correctly folded protein is a function of the hydrophobicity of its floor. Single-point mutations are sometimes useful for enhancing protein solubility, thus enhancing crystallizability. Moreover, mutation of a single floor amino acid can intrude with proteinprotein interactions, thus modifying the overall crystallizability of the target protein. Crystallography could be improved by eradicating websites prone to posttranslational modification which are typically detrimental to crystallization. For example, removal of glycosylation websites by changing asparagines with other residues. Removal of flexible glycosidic teams via deglycosylating enzymes can also be attainable [7]. In distinction to classical X-ray tubes, the synchrotron radiation is produced when electrons are accelerated centripetally through the use of appropriate bending magnets. Evolution of facilities from first- to second- and third-generation absolutely exploited insertion units. X-ray beams produced at third-generation synchrotron amenities are laser-like and are characterized by a high-brilliance beam. They permit the discount of sample publicity time from hours to minutes to seconds. This was paralleled by the event of detectors with tremendously lowered publicity occasions.
Purchase cheap molenzavir on-line
The parenchymal cells are of two types: principal or chief cells and oxyphil cells. The chief cells type the main population and secrete parathyroid hormone called parathormone. The superior parathyroid gland develops from the fourth pharyngeal pouch and eventually lies on the posterior surface of the thyroid lobe at the degree of the isthmus. Clinical correlation · Hypoparathyroidism could occur spontaneously or due to inadvertent removal of parathyroid glands during thyroidectomy. The elevated amount of parathormone: (a) removes excessive calcium from bones, which makes the bones gentle due to decalcification resulting in a clinical condition known as generalized osteitis fibrosa, and (b) could trigger formation of stones within the kidney. The higher half of trachea is situated within the neck (cervical part) whereas the decrease half lies in the superior mediastinum of the thoracic cavity (thoracic part). It is about three mm in newborns and remains so as much as the third year of life; thereafter the lumen increases by 1 mm each year up to 12 years, after which it stays fairly fixed. This data is essential for the anesthetists to select the appropriate size of tracheal tube to be inserted into the trachea in children during general anesthesia. As the thymic diverticulum migrates inferiorly within the neck, it pulls inferior parathyroid with it. Consequently, the inferior parathyroid involves lie lastly on the posterior floor of the thyroid lobe close to the decrease pole. The cartilages are poor posteriorly the place the hole is crammed by connective tissue and involuntary muscle referred to as trachealis. Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands, Trachea, and Esophagus 165 esophagus throughout deglutition. The parasympathetic fibres are derived from vagus by way of the recurrent laryngeal nerve. They are secretomotor and sensory to the mucus membrane and motor to the trachealis muscle. It extends downwards and slightly backwards in entrance of the esophagus following curvature of the cervical spine and enters the thoracic cavity in the median airplane with slight deviation on the best aspect. Clinical correlation Tracheostomy: It is a life-saving surgical process done in instances of laryngeal obstruction. The tracheostomy is usually accomplished in the retrothyroid area after displacing the isthmus of the thyroid gland upwards or downwards. After displacing the isthmus the trachea is opened by a vertical incision within the area of the third and 4th or 2nd and third tracheal rings. The low tracheostomy is risky in children owing to shortness of the neck and presence of thymus and left brachiocephalic vein and sometimes brachiocephalic artery. The esophagus is kept collapsed anteroposteriorly between trachea and vertebral column. The esophagus begins as a continuation of pharynx on the lower border of cricoid cartilage reverse the lower border of C6 vertebra. It passes downwards in entrance of the vertebral column behind trachea, traverses superior and posterior mediastina of thorax, passes by way of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm and ends at the cardiac orifice of the abdomen within the abdomen about 2. The pharyngoesophageal junction is the narrowest a half of the digestive tube besides that of the vermiform appendix. The prevertebral layer of deep cervical fascia forms a movable base on which the trachea and esophagus move up and down during swallowing and phonation. The veins from this half drain into inferior thyroid veins and left brachiocephalic vein. The lymph vessels from the cervical a half of esophagus drain into pretracheal and deep cervical lymph nodes. Clinical correlation · the left margin of the esophagus initiatives laterally from behind the trachea in the region of the neck. Therefore the cervical part of esophagus could be mobilized and exposed surgically extra easily from the left side. This procedure helps to obtain tissue biopsy or removing of swallowed foreign body. For the thoracic and stomach a half of the esophagus, see Textbook of Anatomy: Upper Limb and Thorax, Vol. Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands, Trachea, and Esophagus 167 Golden Facts to Remember " Largest endocrine gland of the physique " Earliest glandular tissue to develop and become practical " Most vascular endocrine gland within the physique " Most widespread type of incomplete descent of thyroid " Most frequent web site of thyroglossal cyst " Most common explanation for hypercalcemia in grownup " Most widespread mode of clinical presentation of hyperparathyroidism " Most widespread cause of hypoparathyroidism " Most preferred site of the tracheostomy " Commonest website of the cancer esophagus " Most common web site of the adenocarcinoma of esophagus Thyroid gland Thyroid tissue Thyroid gland (adrenal medulla can be equally vascular) Lingual thyroid Subhyoid Primary hyperparathyroidism Renal stones Inadvertent elimination throughout surgical procedure.
Buy molenzavir in united states online
The anterior and posterior roots pass to their appropriate intervertebral foramina, where each evaginates dura mater individually earlier than uniting to form the nerve trunk. The ganglion on the posterior root lies in the intervertebral foramen, within the tubular evagination of dura and arachnoid proximal to the point of union of anterior and posterior nerve roots. At all levels from C1 to L1 vertebrae, the anterior and posterior nerve roots cross in front of and behind the ligamentum denticulatum, respectively. Spinal segments: the portion of spinal twine which provides origin to a pair of spinal nerves is termed spinal phase. Due to relative shortening of the spinal twine as compared to the vertebral canal, the spinal segments lie above their corresponding vertebral degree, a fact of nice clinical significance in determining the extent of vertebral injury from signs and symptoms produced as a outcome of harm to a specific segment. It presents two enlargements in these regions, which provide the higher and lower limbs and associated girdles. The two enlargements are as follows: 306 Textbook of Anatomy: Head, Neck, and Brain Table 20. The vertebral ranges of those enlargements are fairly different from that of spinal segments, viz. These enlargements in spinal wire are because of significantly increased mass of motor cells in the anterior horns of gray matter in these spinal segments. The shape of sections is given on the left facet whereas the shape of anterior and posterior horns is given on the best side. Grey Matter the gray matter of spinal cord consists of (a) nerve cells, (b) neuroglia, and (c) blood vessels. Types of motor neurons in the anterior horn (a) Alpha neurons: They are large multipolar cells (25 m or more in diameter) and provide the extrafusal skeletal muscle fibres. Types of motor neurons in the lateral horn They are preganglionic autonomic neurons. The axons of motor neurons go away the spinal wire as the final widespread path (Sherrington) via the ventral roots of the spinal nerves and attain the skeletal muscular tissues. Internal Structure the spinal cord consists of a central mass of grey matter made up of nerve cells and peripheral mass of white matter made up of fibre tracts. In a cross section of the wire, the grey matter is seen as an H-shaped (or butterfly shaped) fluted column, extending all through the size of the spinal cord. It is split into symmetrical proper and left comma-shaped plenty, which are linked throughout the midline by a transverse gray commissure. The lateral comma-shaped mass of gray matter is divided by a transverse gray commissure right into a slim elongated posterior horn and broad anterior horn. In the thoracic segments and upper two lumbar segments (T1 to L2), a triangular projection juts out from the side of the lateral gray mass between the anterior and posterior horns, practically reverse to the grey commissure. The posterior horns are connected to the surface by a gelatinous substance called substantia gelatinosa. Sensory neurons: these are present within the posterior horn and concerned in relay of sensory info to the totally different parts of the brain forming ascending tracts; or to the opposite segments of spinal cord forming intersegmental tracts. Interneurons: these are small neurons current throughout the grey matter of the spinal wire. These are either inhibitory or excitatory and anxious with integration of segmental activities. They are divided into three main groups or nuclei: (a) medial, (b) lateral, and (c) central. Medial group extends alongside most of the size of the spinal twine and innervate the axial musculature of the neck and trunk. Lateral group is confined to the cervical and lumbosacral enlargements and supply the limb muscle tissue. Phrenic nucleus in the cervical area (extending from C3 to C5 segments) innervates the diaphragm. The substantia gelatinosa is steady above with the nucleus of spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve. Nucleus proprius is a gaggle of enormous nerve cells located anterior to the substantia gelatinosa and constitutes the primary bulk of cells present within the posterior grey column.
Order molenzavir 200mg with visa
What You Can Do · If your child has a neck or back harm, name 911 or your local emergency quantity immediately. To relieve the stress, your doctor might break up the cast, open a window in it, or exchange it with a larger one. Protect the limb from unnecessary motion through the use of a rolled-up newspaper, magazine, or similar object for a splint (1) and then fashioning a sling from a scarf, torn sheets, or other material (2). An injured leg ought to be immobilized and elevated till your pediatrician or emergency doctor can see the kid (3). If your youngster suffers a tough blow to the pinnacle, she will need to be evaluated by a doctor. Even with out lack of consciousness, if your youngster has vital memory loss, disorientation, altered speech, visual changes, or nausea and vomiting after a head damage, call 911, your native emergency quantity, or your pediatrician. A concussion is any damage to the mind that disrupts regular mind function on a quick lived or everlasting basis. A concussion requires careful evaluation and monitoring by your pediatrician to be positive that symptoms have completely resolved before clearing your baby to resume full activities (both college and sports activities related). Prevention · Always use restraints when using child tools corresponding to carriers, strollers, and high chairs. All children should ride within the rear seat, properly buckled into safety belts or automobile safety seats. The probability of injury will increase during occasions of family stress (eg, an sickness, a death within the household, a pregnancy or delivery, change in environment). Installing and implementing childproofing measures reduces the chances of an injury to your child by making her setting as secure as possible. Certainly, by the point your baby can sit on his personal and use his arms for exploration (about 6 months of age), your own home ought to be utterly childproofed. How far and fast he can transfer, the heights he can attain, and the objects that entice his consideration will change continually. They must also be nontoxic and sturdy, without small or pointed parts or ribbons and strings. Frequent room-by-room checking for attainable hazards is extraordinarily important at this age. When your baby grabs for an unsafe object similar to your purse, offer him a permitted object corresponding to a book as a distraction. Use a firm "no" for dangerous conditions, corresponding to a scorching radiator, and clarify why ("No! Explain why these guidelines should be obeyed, however stay vigilant about supervising your child and preventing entry to hazardous conditions. Children have an uncanny method of finding potentially poisonous items, even in uncommon locations. Remember that these caps are child-resistant, not childproof, so maintain them in a locked cupboard. Never call drugs or nutritional vitamins "sweet" when giving them to your youngster to get her to take them. Check the label each time you give treatment to ensure you are giving the proper medicine within the correct dosage. Try to find the most secure ones for the job, and purchase only what you need to use right away. Glasses should be emptied and rinsed instantly after a celebration at which alcohol is served. Secondhand smoke is dangerous to kids and raises their threat for ear infections, asthma, headaches, and different health issues. This includes cigarettes, cigars, smoked butts, pipe and chewing tobacco, snuff, and nicotine gum, patches, and sprays. Laundry detergents should be stored in a excessive or locked cabinet, not on prime of Poison Prevention Every day, 300 children between the ages of 1 and 19 years are handled in emergency departments for poisoning, and a pair of die. Personal-care products, cosmetics, and household cleaning products are common causes of childhood poisoning, with over-thecounter drugs on the prime of the list. Single-use detergent packets should be saved out of sight and reach of children in a child-resistant container. Be cautious using the garage door opener, and ensure the automated reversing mechanism is correctly adjusted. Be certain that your youngster care provider and anyone else caring in your baby is conscious of when and tips on how to use these numbers.
Real Experiences: Customer Reviews on Molenzavir
Tuwas, 27 years: Make sure they know their name and address (as nicely as when to give it out and when not to! Ligaments Fibrous capsule: It is thin and unfastened, and attached to the periphery of articular aspects.
Hanson, 29 years: The arachnoid mater is separated from the dura mater by a capillary area called the subdural space containing a movie of fluid. The nucleus of superior colliculus consists of cells which are involved generally mild reflexes.
Gambal, 59 years: The 1918, 1957, and 1968 pandemics have been attributable to viruses containing H1N1, H2N2, and H3N2, respectively. These elevations are produced by the descending fibres of the corticospinal tracts concerned in the acutely aware management of the skeletal muscular tissues.
Varek, 26 years: For particulars of options on the dorsal floor of pons, see the floor of the 4th ventricle described in detail in Chapter 25. Incorporation of a methyl group at the proximal place with respect to the amide bond and having (R)-configuration consistently showed an improvement in exercise (compounds 12 and 16 vs compounds 13 and 17, respectively).
8 of 10 - Review by C. Ur-Gosh
Votes: 174 votes
Total customer reviews: 174
References
- Wilson NJ, Clarkson PM, Barratt-Boyes BG, et al: Long-term outcome after the mustard repair for simple transposition of the great arteries. 28-year follow-up, J Am Coll Cardiol 32:758-765, 1998.
- Edmond J, Popjak G. Transfer of carbon atoms from mevalonate to n-fatty acids. J Biol Chem 1974;249:66.
- Mehra MR, Canter CE, Hannan MM, et al. The 2016 International Society for Heart Lung Transplantation listing criteria for heart transplantation: a 10-year update. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2016;35:1-23.
- Yocum DE, Hodes R, Sundstrom WR, et al: Use of biofeedback training in treatment of Raynaud's disease and phenomenon, J Rheumatol 12:90-93, 1985.
- Steinbeck G, Andersen D, Seidi K, et al. Defibrillator implantation early after myocardial infarction. N Eng J Med 2009;361:1427-1436.
- Lee TH, Goldman L. The coronary care unit turns 25: historical trends and future directions. Ann Intern Med. 1988;108:887.
- Pearl FL. Muscle-splitting extraperitoneal lumbar ganglionectomy. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1937;65:107-112.

